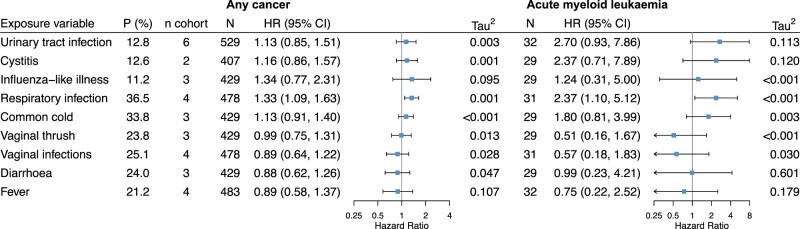
Figure 2.
Associations of each maternal infection during pregnancy with risk of any childhood cancer and acute myeloid leukaemia. P (%), prevalence of the infection, weighted by the inverse of the sampling probability in Danish National Birth Cohort and Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study; n cohort, number of cohorts with available infection data; N, total number of cases in the pooled dataset; HR (95% CI), hazard ratio and 95% confidence interval; Tau2, variance of effect sizes across cohorts; and its square root (Tau) is the standard deviation of the distribution of effect sizes across cohorts. Hazard ratios were obtained using multilevel Cox modelling with random baseline hazards and random coefficients of the infection and were adjusted for maternal age, education level, smoking during pregnancy, pre-pregnancy body mass index, parity and diabetes. Models for influenza-like illness, common cold and respiratory tract infection were additionally adjusted for birth seasons. Compatibility categories of infection variables across cohorts: high for urinary tract infection, cystitis and vaginal thrush; moderate for influenza-like illness, vaginal infections and diarrhoea; low for respiratory tract infection, common cold and fever