FIGURE 3.
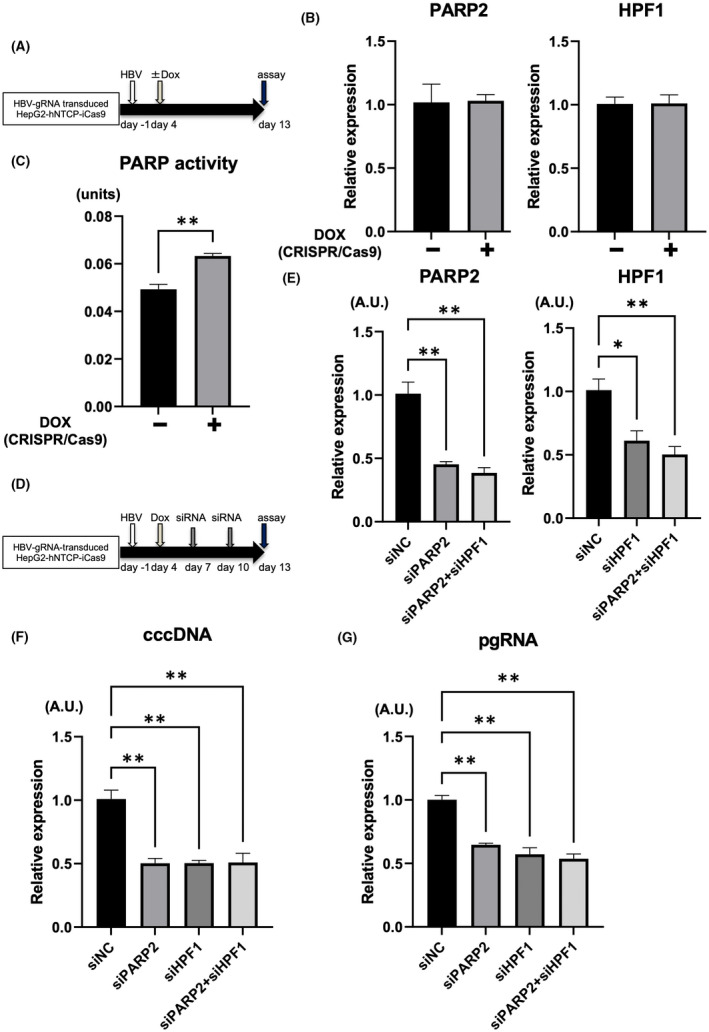
Inhibition of poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose) polymerase 2 (PARP2)–HPF1 enhances the antiviral effect of HBV‐CRISPR in HBV‐infected hepatoma cells. (A–C) HepG2‐hNTCP‐C4‐iCas9 cells transduced with HBV gRNA were treated with or without DOX 4 days after HBV inoculation (10,000 GEq/cell). (A) Experimental protocol. (B) Messenger RNA (mRNA) levels of PARP2 and HPF1 in HepG2‐hNTCP‐C4‐iCas9 cells transduced with HBV gRNA 13 days after HBV inoculation (n = 4). (C) PARP activity in HepG2‐hNTCP‐C4‐iCas9 cells transduced with HBV gRNA 13 days after HBV inoculation (n = 4, **p < 0.01). (D–G) HepG2‐hNTCP‐C4‐iCas9 cells transduced with HBV gRNA were treated with DOX 4 days after HBV inoculation (10,000 GEq/cell) and were then treated with small interfering RNA (siRNA) 7 and 10 days after HBV inoculation. (D) Experimental protocol. (E) mRNA levels of PARP2 and HPF1 in HBV gRNA–transduced HepG2‐hNTCP‐C4‐iCas9 cells 13 days after HBV inoculation (n = 4; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). (F) Expression levels of cccDNA in HBV gRNA–transduced HepG2‐hNTCP‐C4‐iCas9 cells 13 days after HBV inoculation (n = 4; **p < 0.01). (G) Expression levels of pgRNA in HBV gRNA–transduced HepG2‐hNTCP‐C4‐iCas9 cells 13 days after HBV inoculation (n = 4; **p < 0.01). HPF1, Histone PARylation factor 1.
