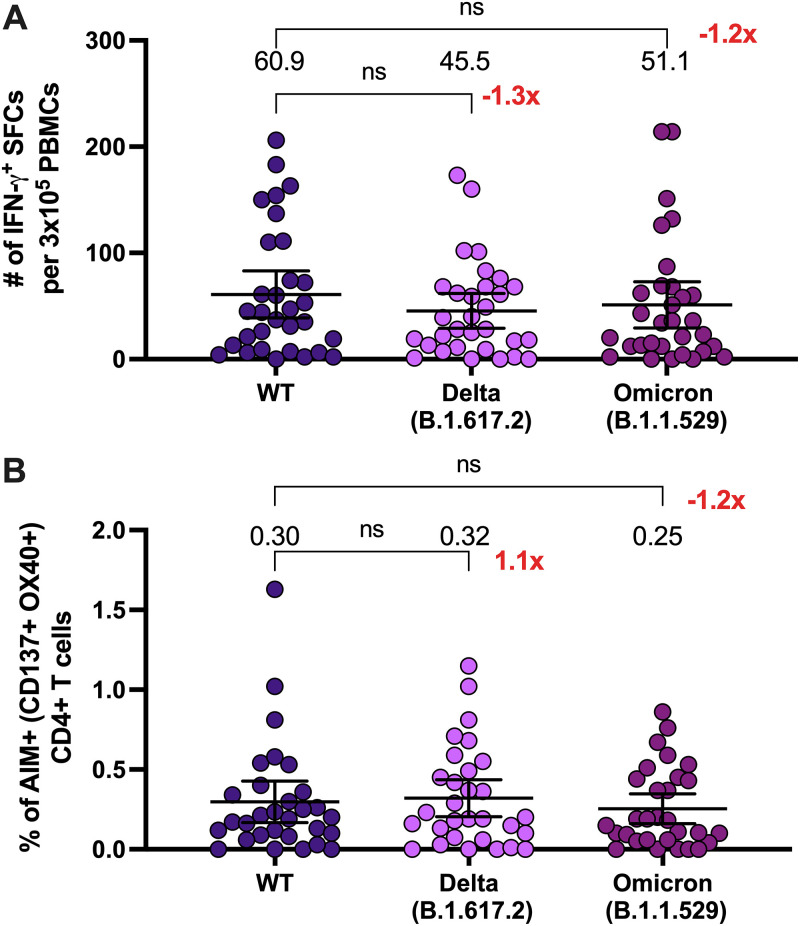
FIG 5.
A booster dose of CoronaVac induces changes in the number of IFN-γ-secreting cells and in activation-induced marker (AIM) expression in CD4+ T cells specific for the Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 variants. (A) Changes in the secretion of IFN-γ were determined as the number of spot-forming cells (SFCs). Data were obtained upon stimulation of PBMC with MP-S of variants of concern of SARS-CoV-2 for 48 h in samples obtained 4 weeks after the booster dose. Data shown represent means + 95% CI. Data from 30 volunteers were analyzed 4 weeks after the booster dose to compare the MP-S of the variants of concern. Data from ELISPOT were analyzed separately by Friedman test against the WT MP-S. No significant differences were obtained. (B) AIM+ CD4+ T cells were quantified in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of 30 volunteers 4 weeks after they received a booster dose of CoronaVac by use of flow cytometry, upon stimulation with megapools of peptides derived from proteins of variants of concern of SARS-CoV-2. The percentage of activated AIM+ CD4+ T cells (OX40+ CD137+) was determined after stimulation for 24 h with MP-S + R in samples obtained 4 weeks after the booster dose. The number at the right represents the fold increase of the GMU 4 weeks after the third dose, compared with the respective times after administering the second dose. Data shown represent means + 95% CI. Data from flow cytometry were normalized against DMSO. No significant differences were obtained between WT and the variant MP stimulation.