FIG 5.
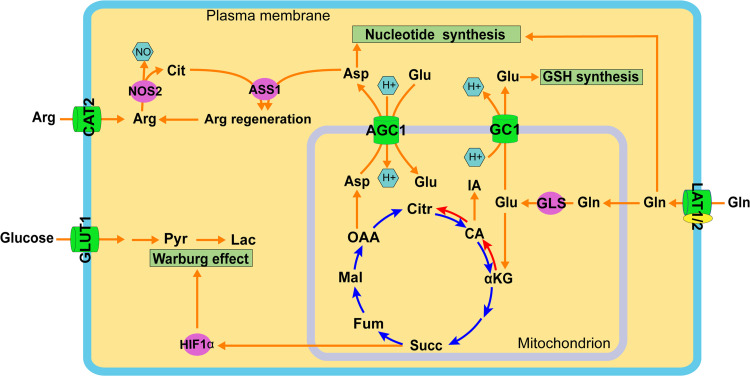
Coordination of glucose and glutamine catabolism during M1-like polarization. M1-like polarization is marked with increased catabolism of glucose and glutamine (Gln) in distinctive subcellular compartments but with coordinated functions. Increased glucose uptake, mediated by GLUT1, and its catabolism in the glycolysis pathway in the cytosol result in the production of lactate (Lac). Increased Gln uptake, probably mediated by neutral amino acid antiporters LAT1 and/or LAT2, and its direct metabolite glutamate (Glu) participate in multiple pathways of the metabolic remodeling program of M1-like macrophages. Glu, the product of the glutaminolysis pathway by glutaminase (GLS) in mitochondria, enters the TCA cycle for anaplerosis reactions. Glu replenishes the TCA cycle leading to the generation of itaconate (IA) and succinate, which promotes stabilization of HIF-1α and the subsequent Warburg effect. Gln also contributes both carbon and nitrogen to the formation of the nonessential amino acid aspartate (Asp), probably as a result of transamino reactions in mitochondria, which is then involved in biosynthetic pathways in the cytosol, including nucleotide synthesis and intracellular arginine regeneration by coupling with nitric oxide synthase 2 (NOS2)-derived citrulline (Cit) via argininosuccinate synthase 1 (ASS1) to sustain NO generation by NOS2. The export of mitochondrial Asp to the cytosol is mediated by the functional coupling between two mitochondrial carriers: the glutamate carrier 1 (GC1) exports the mitochondrial Glu deriving from GLS activity to cytosol, and cytosolic Glu then enters mitochondria by serving as a substrate of aspartate/glutamate carrier 1 (AGC1) for the net export of mitochondrial aspartate to the cytosol. Cytosolic Glu also participates in intracellular redox homeostasis involving the synthesis of glutathione (GSH). Abbreviations: CAT2, cationic amino acid transporter 2; αKG, α-ketoglutarate; Arg, arginine; CA, cis-aconitate; Citr, citrate; Fum, fumarate; Mal, malate; OAA, oxaloacetate; Pyr, pyruvate.