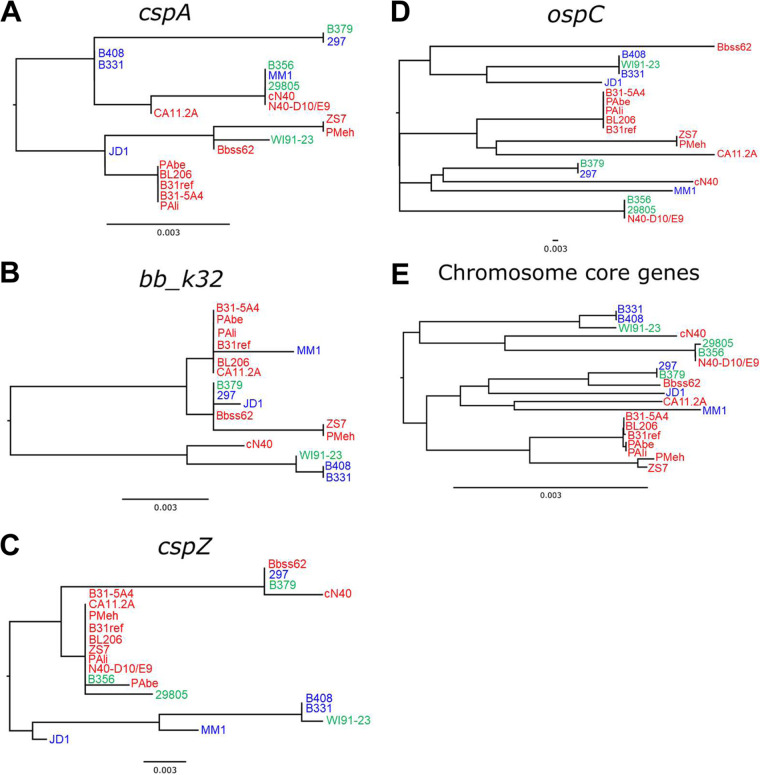
FIG 2.
Phylogenetic trees of B. burgdorferi anti-complement proteins associate ospC and chromosomal core genes with host-specific complement inactivation activity. Individual phylogenies of cspA (A), bb_k32 (B), cspZ (C), ospC (D), and chromosome core genes (E) represent evolutionary relationships among the 20 indicated B. burgdorferi strains with known complement evasion phenotypes. Labels are color-coded to represent strains that can efficiently inactivate complement from mouse (blue), quail (green), or both hosts (red). Strains that do not harbor particular loci are excluded from those respective trees.