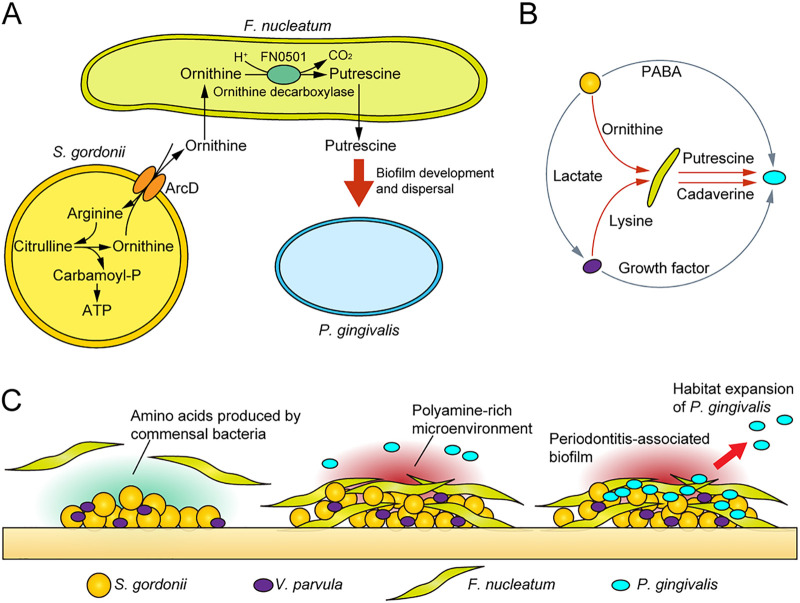
FIG 7.
Proposed schematic model of polymicrobial metabolic synergy in the etiology of periodontal disease. (A) Pathogenic cross-feeding among three key species. The arginine deiminase system in S. gordonii facilitates putrescine production by F. nucleatum, which further promotes the biofilm overgrowth and dispersal of P. gingivalis. (B) A fuller picture of F. nucleatum-mediated trophic networks. Gray arrows denote known metabolic cross-feeding interactions, while red arrows denote those found in the present study. (C) Model depicting metabolic integration by F. nucleatum within polymicrobial communities. Commensal-triggered polyamine production by F. nucleatum contributes to shaping the periodontitis-associated community.