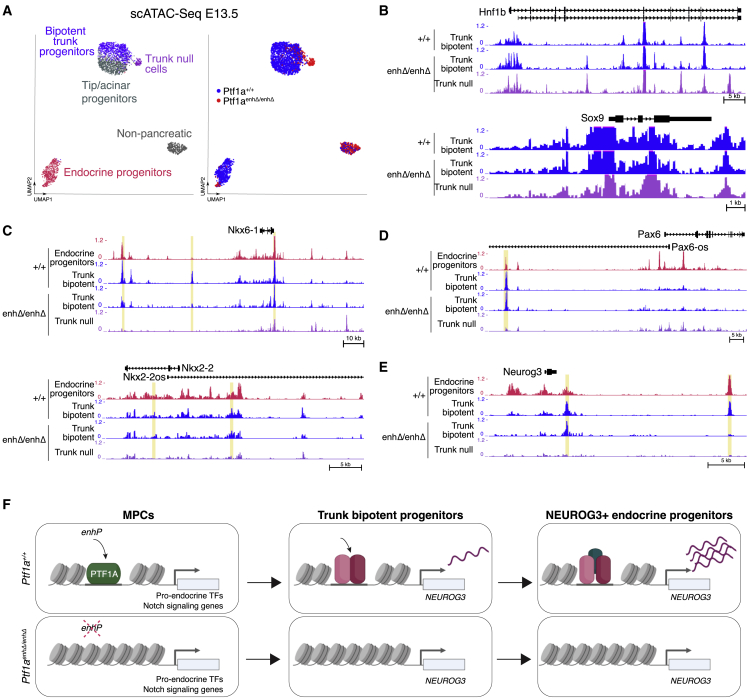
Figure 6.
PTF1A in MPCs triggers sequential chromatin changes in Neurog3
(A) scATAC UMAP plots of E13.5 Ptf1aenhΔ/enhΔ and Ptf1a+/+ pancreas identifies NEUROG3+ endocrine progenitors, pro-acinar progenitors, trunk bipotent progenitors, and mutant-specific trunk null cells. Nuclei are colored by cell type (left) or genotype (right).
(B–E) Pseudo-bulk scATAC-seq profiles from E13.5 Ptf1a+/+ and Ptf1aenhΔ/enhΔ trunk and trunk null cells. Regions downregulated in trunk null cells (log2-fold-change < −0.5, binomial test FDR < 0.1) are highlighted in yellow. (B) Depicts Hnf1b and Sox9 loci and (C–E) show reduced accessibility in Ptf1aenhΔ/enhΔ trunk null cells at indicated sites of endocrine regulatory loci. Profiles in NEUROG3+ cells are shown for comparison. In (E), E13.5 Ptf1a+/+ trunk progenitors exhibit an active chromatin state at Neurog3 that is similar to NEUROG3+ progenitors, whereas this is abrogated in Ptf1aenhΔ/enhΔ trunk null cells and is altered at several sites in other Ptf1aenhΔ/enhΔ trunk cells.
(F) Proposed model illustrating sequential steps triggered by PTF1AenhP activation of PTF1A. PTF1A binds and remodels chromatin at pro-endocrine gene loci in MPCs. Active chromatin states are maintained at endocrine genes such as NEUROG3 in bipotent progenitor trunk cells, enabling full activation of NEUROG3 in endocrine-committed progenitors. PTF1AenhP deletion prevents this process, causing reduced endocrine differentiation. See also Figure S6.