Figure 7.
PTF1AenhP creates an active enhancer cluster in mouse and human MPCs
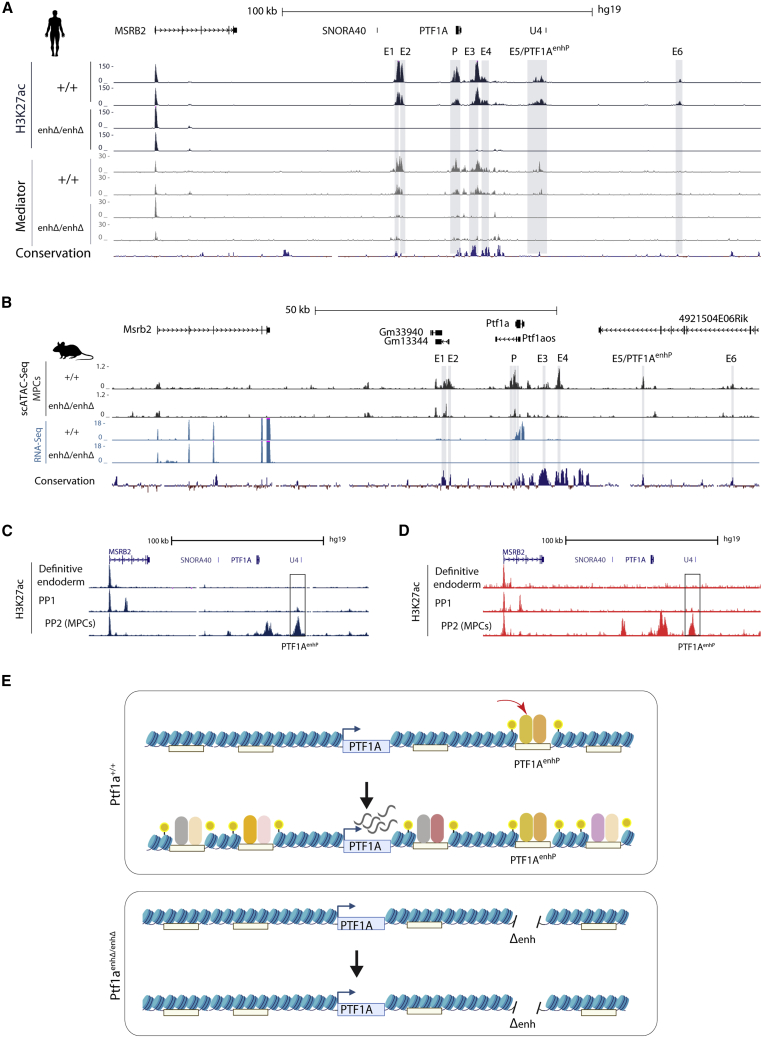
(A) Regulatory landscape of the human PTF1A locus in PTF1A+/+ and PTF1AenhΔ/enhΔ MPCs. Six H3K27ac-enriched putative enhancers and the PTF1A promoter, most of which show strong mediator (MED1) binding, are shaded in gray. All show absent activity in PTF1AenhΔ/enhΔ MPCs (q < 0.05). ChIP-seq tracks show a MACS2 −log10 p values.
(B) scATAC-seq profiles for MPCs from Ptf1a+/+ and Ptf1aenhΔ/enhΔ E10.5 pancreatic buds showed chromatin accessibility at Ptf1a and E1-E6 regions orthologous to human enhancers, highlighted in gray. All showed loss in Ptf1aenhΔ/enhΔ cells (q < 0.1, log2FC < −0.5). Conservation tracks show multiple alignments between 100 vertebrate species.
(C and D) H3K27ac at the PTF1A locus in 2 hPSC-derived pancreatic progenitor datasets (Alvarez-Dominguez et al., 2020; Geusz et al., 2021). Both used a protocol that generates two stages of early pancreatic progenitors: PP1 PDX1+ cells that do not express MPC markers such as NKX6-1, PP2 PDX1+, and NKX6.1+ cells that are comparable with stage 4 MPCs from the current study. In both datasets, H3K27ac enrichment at PTF1AenhP preceded that of all other enhancers.
(E) Summary model illustrating how PTF1AenhP precedes and activates the enhancer cluster in the PTF1A locus. See also Figure S7.