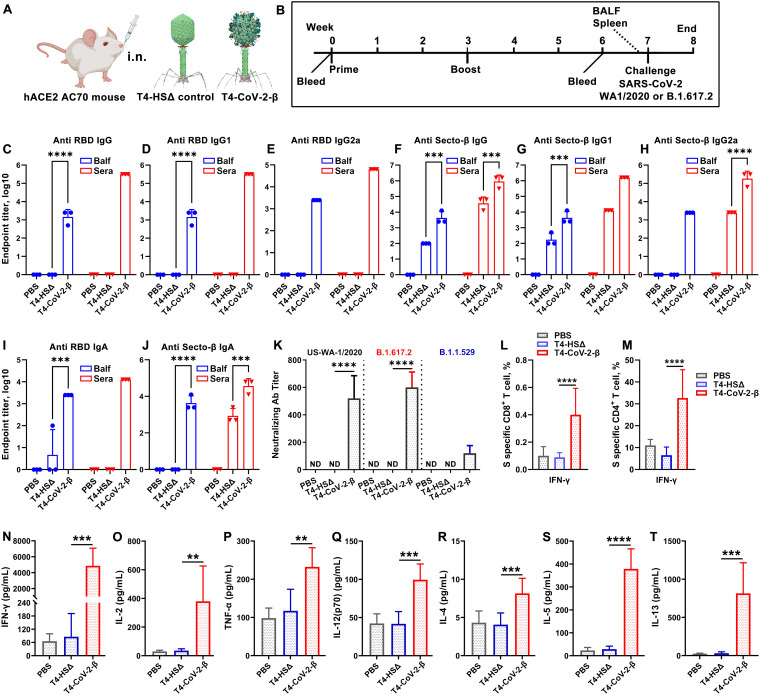
FIG 5.
Intranasal T4-CoV-2-β vaccination stimulated robust mucosal and systemic humoral and cellular immune responses in hACE2-transgenic mice. (A) Schematic of i.n. mouse vaccination with T4-HSΔ control or T4-CoV-2-β vaccine. (B) Scheme for vaccination and challenge. (C to J) Antibody responses in sera (red) and BALF (blue) of immunized mice on day 21 after the boost. ELISA was applied to determine reciprocal endpoint antibody titers of anti-RBD IgG (C), anti-RBD IgG1 (D), anti-RBD IgG2a (E), anti-Secto-β IgG (F), anti-Secto-β IgG1 (G), anti-Secto-β IgG2a (H), anti-RBD IgA (I), and anti-Secto-β IgA (J). (K) Neutralizing antibody titers in sera were determined by a Vero E6 cell cytopathic assay using WA-1/2020, B.1.617.2 (Delta), and B.1.1.529 (Omicron) strains. (L and M) Cellular immune responses after stimulation with Secto-β protein. The percentages of IFN-γ+ CD8+ (L) and IFN-γ+ CD4+ (M) cells were plotted. (N to T) Splenocyte cytokine responses to Secto-β protein stimulation in immunized hACE2-transgenic mice. Representative Th1 (N to Q) and Th2 (R to T) cytokines are shown. For panels C to M, two-way (C to J, L to M) or one-way ANOVA (K) was performed with a Tukey post hoc test. For panels N to T, a nonparametric Student t test was performed. The data are from three pooled independent experiments (n = 15 for T4-HSΔ and PBS sera analysis, n = 21 for T4-CoV-2-β sera analysis, and n = 5 for BALF analysis). The data are representative of two (K) or five (L to T) biological replicates. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.