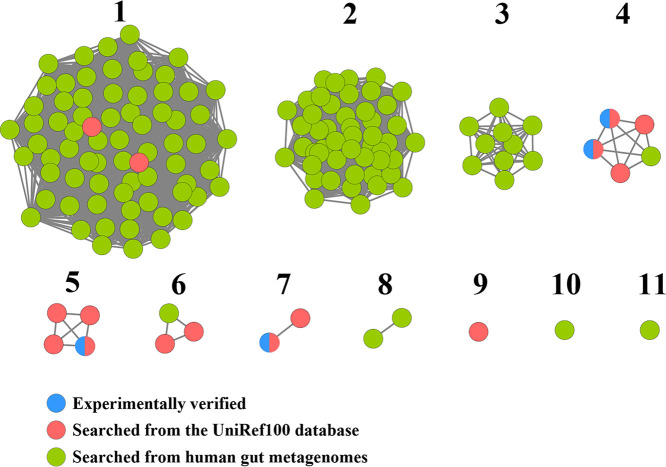
FIG 1.
Sequence similarity networks (SSNs) of 135 protein sequences (green) identified from human gut microbiome whole-genome sequences, based on an alignment score of 70 (approximately 90% sequence identity). The BaiE sequences that had been previously experimentally verified (blue) or obtained from the UniRef100 database (red) were also used to generate the SSNs. Each node in the SSNs represents a protein, and alignment scores between proteins in different clusters are <70. Proteins within the same clusters have sequence identities of >92.4%. Numbers reflect arbitrary naming of clusters.