Extended Data Figure 7: Discrepancies between readers and deep learning model.
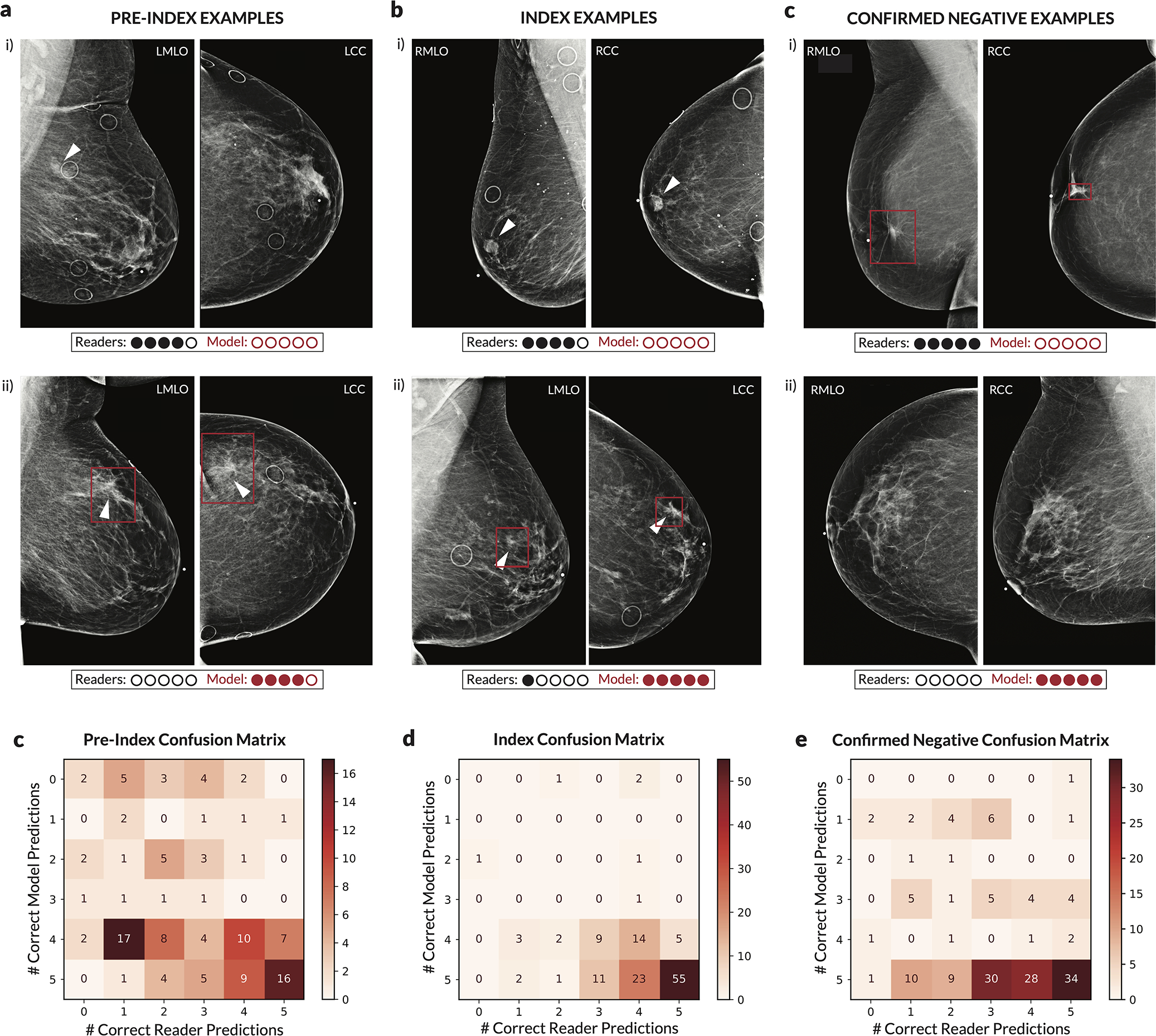
For each case, the number of readers that correctly classified the case was calculated along with the number of times the deep learning model would classify the case correctly when setting a score threshold to correspond to either the specificity of each reader (for index and pre-index cases) or the sensitivity of each reader (for confirmed negative cases). Thus, for each case, 0–5 readers could be correct, and the model could achieve 0–5 correct predictions. The evaluation of the model at each of the operating points dictated by each reader was done to ensure a fair, controlled comparison (i.e., when analyzing sensitivity, specificity is controlled). We note that in practice a different operating point (i.e., score threshold) may be used. The examples shown illustrate discrepancies between model and human performance, with the row of dots below each case illustrating the number of correct predictions. Red boxes on the images indicate the model’s bounding box output. White arrows indicate the location of a malignant lesion. a) Examples of pre-index cases where the readers outperformed the model (i) and where the model outperformed the readers (ii). b) Examples of index cases where the readers outperformed the model (i) and where the model outperformed the readers (ii). c) Examples of confirmed negative cases where the readers outperformed the model (i) and where the model outperformed the readers (ii). For the example in c.i.), the patient previously had surgery six years ago for breast cancer at the location indicated by the model, but the displayed exam and the subsequent exam the following year were interpreted as BIRADS 2. For the example in c.ii.), there are posterior calcifications that had previously been biopsied with benign results, and all subsequent exams (including the one displayed) were interpreted as BIRADS 2. d) Full confusion matrix between the model and readers for pre-index cases. e) Full confusion matrix between the model and readers for index cases. f) Full confusion matrix between the model and readers for confirmed negative cases.
