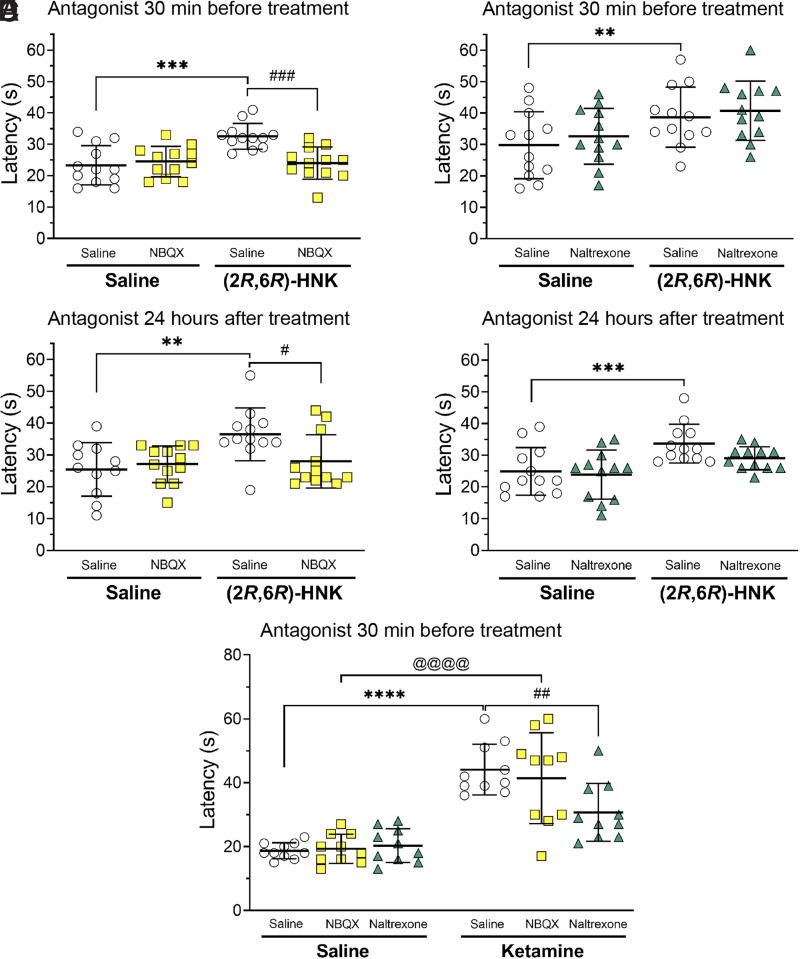
Fig. 3.
The effects of AMPA receptor antagonism with NBQX (10 mg/kg) or opioid receptor antagonism with naltrexone (1 mg/kg) on the initiation or expression of antinociception by (2R,6R)-HNK. The effects of (2R,6R)-HNK (10 mg/kg) were measured 24 hours after injection. Panel A: The NBQX given 30 minutes before (2R,6R)-HNK treatment blocked the initiation of (2R,6R)-HNK antinociception. Panel B: Naltrexone given 30 minutes before (2R,6R)-HNK treatment did not block the initiation of (2R,6R)-HNK antinociception. Panel C: NBQX given 24 hours following (2R,6R)-HNK treatment blocked the expression of (2R,6R)-HNK mediated antinociception. Panel D: Naltrexone given 24 hours following (2R,6R)-HNK treatment did not alter (2R,6R)-HNK antinociception. Panel E: Ketamine (10 mg/kg) mediated antinociception measured 10 minutes following treatment was unaffected by pretreatment with NBQX (10 mg/kg given 30 minutes prior), while naltrexone (1 mg/kg given 30 minutes prior) blocked ketamine antinociception. The error bars represent group means ± S.D. Group comparisons are indicated with horizontal lines. Asterisks represent treatment/saline to saline/saline comparisons: **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001. The # symbol represents treatment/NBQX to treatment/saline comparisons: # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, and ### P < 0.001. The @ symbol represents NBQX/saline compared with NBQX/ketamine: @@@@, P < 0.0001. N = 11–12 for the (2R,6R)-HNK experiments, N = 10 for the ketamine experiment.