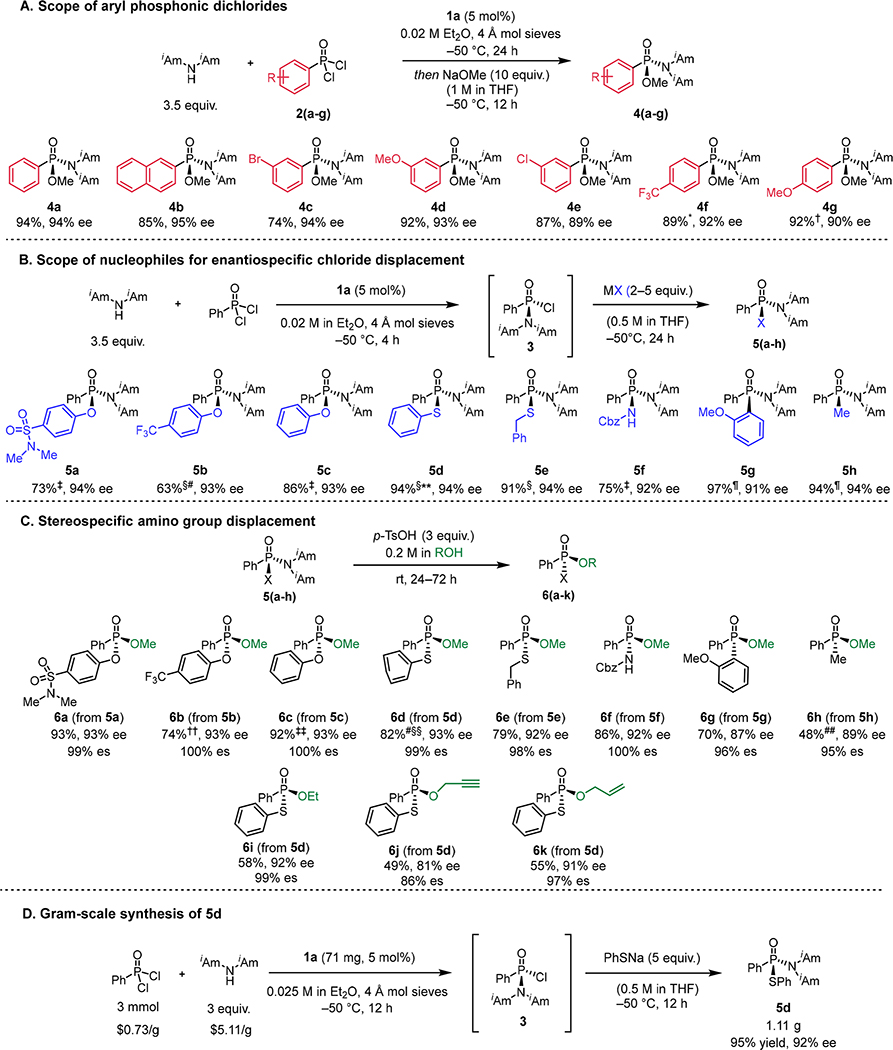
Fig. 3. Scope of enantioselective addition of diisoamylamine to aryl phosphonic dichlorides and stereospecific elaborations.
All yield values correspond to chromatographically purified, isolated products. Concentration values correspond to the initial concentration of the limiting stoichiometric reagent. (A) Substrate scope of addition of diisoamylamine to aryl phosphonic dichlorides catalyzed by 1a. Reactions were carried out on 0.2 mmol scale. The absolute stereochemistry of the products was assigned based on the x-ray crystal structure of 10 and the known optical rotation of 8a (Fig. 4, see supplementary materials). (B) Scope of nucleophiles for enantiospecific substitution with 3. (C) Enantiospecific displacement of the diisoamylamino group with alcohols. See supplementary materials for reaction conditions. (D) Gram-scale synthesis of 5d. Prices from Thermo Fisher Scientific (February, 2022). *Reaction was carried out at −78 °C with 20 mol% catalyst loading. †Reaction was carried out at −40 °C with 4.5 equivalents of diisoamylamine. ‡ Reaction was carried out in a two-pot procedure involving generation of 3 in solution and purification by filtration through silica and subsequent reaction with 2 equivalents of nucleophile. § Reaction was carried out using one-pot procedure without purification of 3 with 5 equivalents of nucleophile. ¶ Reaction was carried out in a two-pot procedure involving generation of 3 in solution and purification by filtration through silica and subsequent reaction with 5 equivalents of nucleophile. #Reaction was carried out on 0.9 mmol scale. **Reaction was carried out on 1.0 mmol scale. ††Reaction was carried out on 0.57 mmol scale. ‡‡Reaction was carried out on 0.24 mmol scale. §§ Reaction was run at 0.3 M concentration instead of 0.2 M. ##H3PO3 was used instead of para-tolylsulfonic acid.