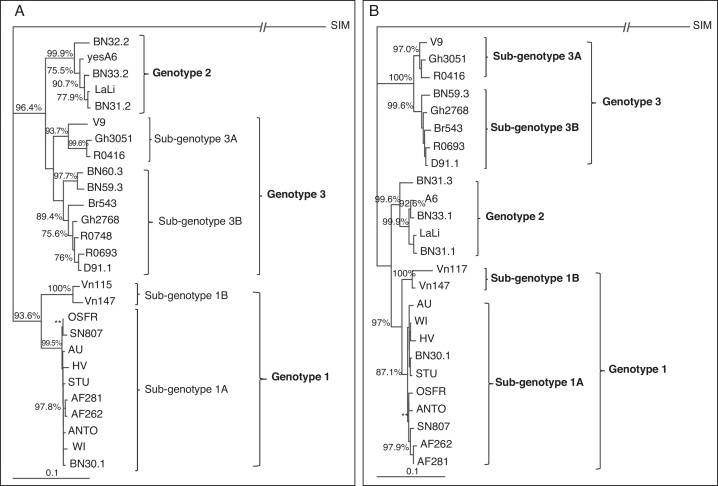
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of the detected human parvovirus B19 (B19V) isolates from acutely infected and asymptomatic children with sickle cell disease. (A) Rooted NJ tree of the reference B19V genotypes and the sequences obtained from the patients with acute (AF282) and asymptomatic infections (AF262) based on a 442 bp fragment of the NS1 region. The simian parvovirus (SIM) is used as an outgroup; (B) Rooted NJ tree of the reference B19V genotypes and the sequences obtained from the patients with acute (AF282) and asymptomatic infections (AF262) based on a 699 bp fragment of the VP1 region. Simian parvovirus is also used as an outgroup. The posterior probabilities (above 75%, using 1000 bootstrap replicates) are indicated at the clusters. The statistical evaluation of some important branches was also performed by the Maximum Likelihood method (**p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05).