Figure 4. Clinicopathologic and genomic characteristic of SCLC-P.
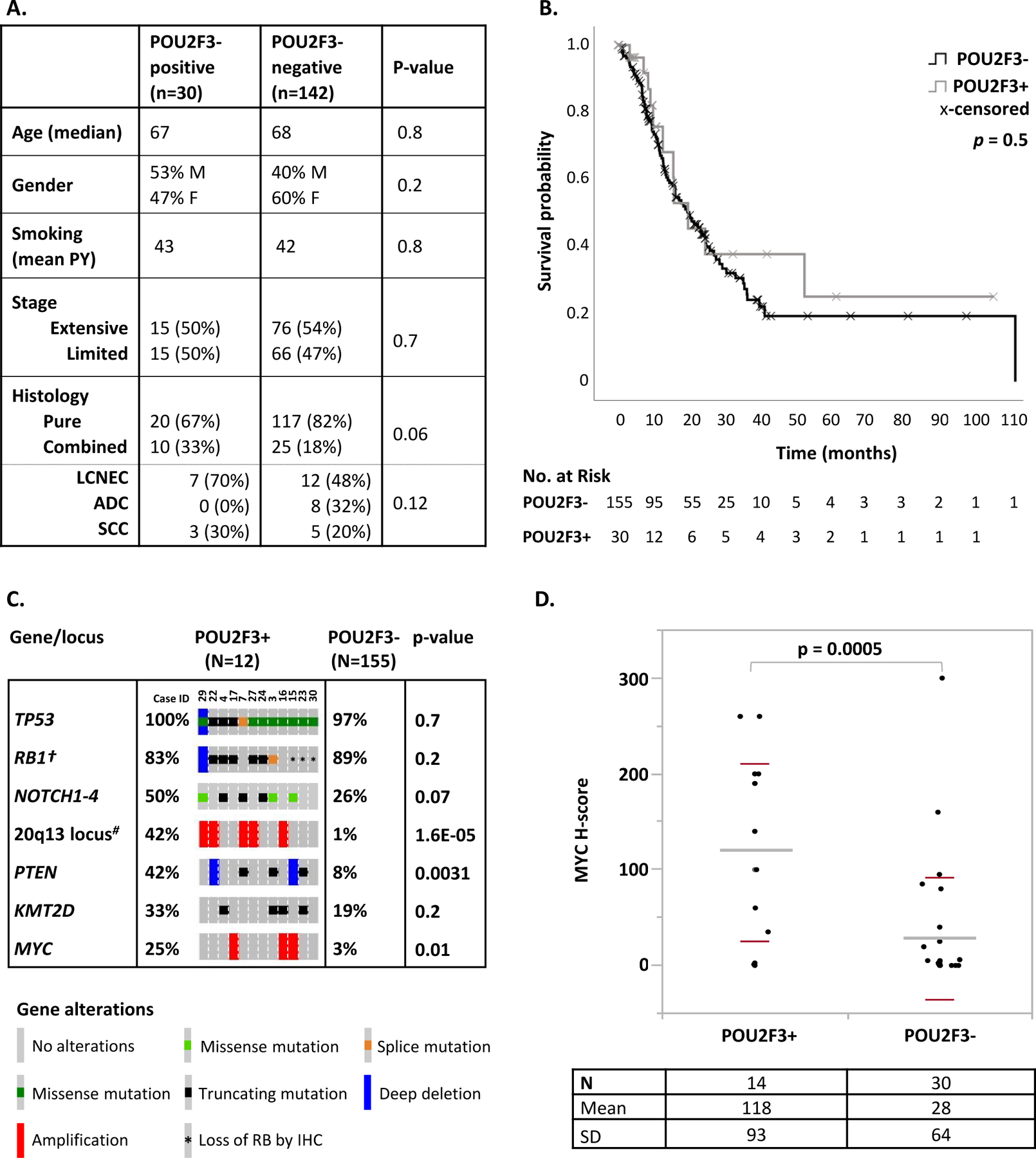
(A) Table comparing clinical and histologic features of SCLC-P (POU2F3-positive) vs other SCLC (POU2F3-negative). (B) Univariate Kaplan-Meyer analysis comparing overall survival in patients with SCLC-P vs other SCLC. (C) Summary of molecular characteristics of SCLC-P. The most prevalent (≥33%) genomic alterations in SCLC-P are shown, as well as genes with divergent distribution in SCLC-P compared to other SCLC. †Rb IHC was performed on all SCLC cases, and the rate of shown RB1 alterations incorporates genomic and IHC findings. #Amplifications of the 20q13 locus involved several genes, including NCOA3 in all 5 cases, and AURKA and GNAS in 3 of 5 cases (Case ID 29, 22 and 16). (D) MYC expression by IHC in SCLC-P vs other SCLC.
Abbreviations: ADC adenocarcinoma, IHC immunohistochemistry, LCNEC large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, PY pack years, SCC squamous cell carcinoma
