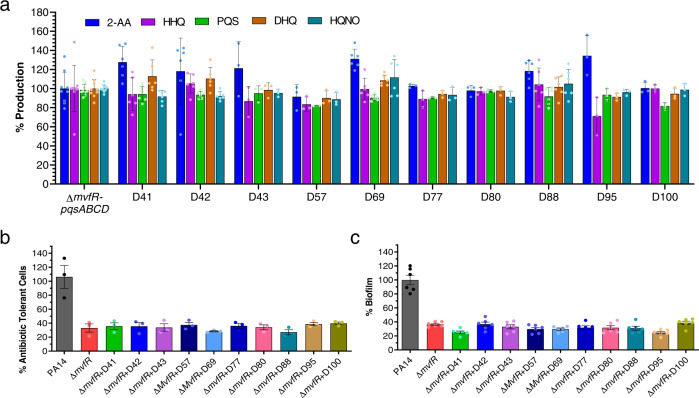
Fig. 4. In vitro assessment of NAMs efficacy indicates no off-target effect.
a Effect of the selected compounds on the MvfR-independent HAQs, 2-AA, and DHQ production. The production of the MvfR-regulated small molecules 2-AA, HHQ, PQS, DHQ, and HQNO was measured in the cultures at OD600nm = 3.0 in the presence of 50 µM of the indicated compounds using a MvfR mutant strain that constitutively expresses the pqsABCDE genes. The cells were grown with or without (vehicle only) compound, and the small molecules production was measured using liquid chromatography-mass spectrophotometry (LC-MS). The percentage production was calculated compared to cells grown with the vehicle control. b AT/P cell formation in the PA14 isogenic mutant ∆mvfR in the presence of the indicated compounds. Cells were grown in the presence of 10 μg mL−1 meropenem, with or without 10 µM of the compounds for 24 h. Values were normalized to cells grown for 4 h in the absence of antibiotics and compounds. The ∆mvfR cells grown with antibiotics and vehicles were considered control, and the percentage values were calculated compared to control. c Biofilm formation of mutant ∆mvfR cells with or without compound. Biofilm was grown in the 96-well microtiter plate at 37 °C for 24 h containing M63 minimal media in the presence of 10 µM of the compounds or vehicle. The biofilm grown with the vehicle was considered as a control. The percentage value was calculated in comparison to the PA14 control. a–c Data represent at least n = 3, each dot on the graph represents one biological replicate. The number of biological replicates for each compound and strain is depicted in the graph. The error bars denote ±SEM. HAQs = 4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines; 2-AA = 2-aminoacetophenone; DHQ = 2,4-dihydroxyquinoline; PQS = 3,4-dihydroxy-2-heptylquinoline; DHQ = 2,4-dihydroxyquinoline; HQNO = 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline N-oxide.