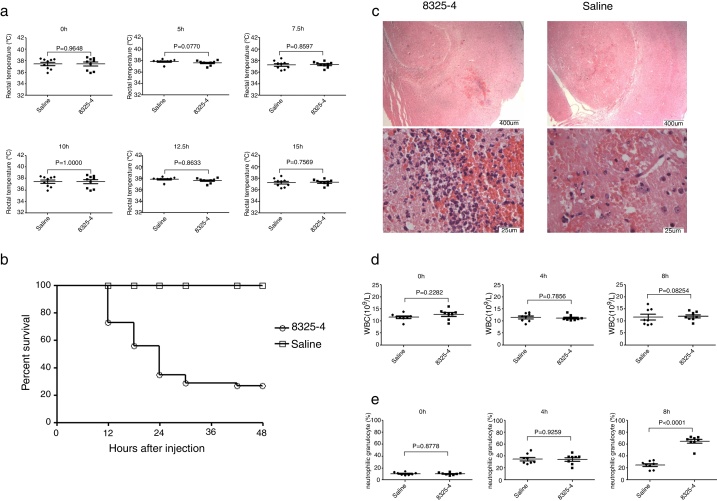
Fig. 1.
Construction of murine intracranial abscesses model caused by S. aureus. (A) Measurement of rectal temperature of mice at different time points after challenge with S. aureus 8325-4 (0 h, 5 h, 7.5 h, 10 h, 12.5 h, 15 h) (n = 9 in each group). (B) Measurement of survival curve of mice in the two groups (n = 52 mice in each group). Mice were challenged with S. aureus 8325-4 or saline. The number of dead mice was recorded. The survival rates of the two groups were calculated individually, p < 0.0001. (C) Histological examination of mouse brain tissue. Brain tissues from the two groups were collected 8 h post-challenge with S. aureus 8325-4 and fixed. The fixed tissues were stained by H&E. (D) White blood cell count of the two groups at different time points (0 h, 4 h and 8 h) post-challenge with S. aureus (n = 8 in each group). (E) Percentage of neutrophils in the two groups at different time points (0 h, 4 h and 8 h) post-challenge with S. aureus (n = 8 in each group).