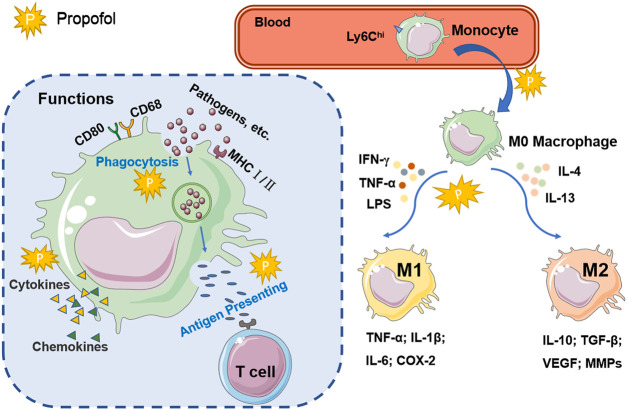
FIGURE 1.
The activation and function of macrophages. Ly6Chi monocytes in the blood enter the damaged tissue and differentiate into macrophages. Macrophages recruited by inflammation or tumors are stimulated by Th1 or Th2 cytokines to differentiate into two activated types: the classical activated type (M1) and the alternating activated type (M2). Activated macrophages express high levels of CD80, CD68, and MHC I/II. Macrophages phagocytize pathogens and cell fragments, recognize specific antigens, and transmit signals to T cells for antigen presentation. Macrophages participate in immune regulation by regulating the secretion of cytokines and chemokines. The explosion-shaped graphic represents propofol, suggesting that it may be involved in the signaling pathways and cellular processes of macrophages.