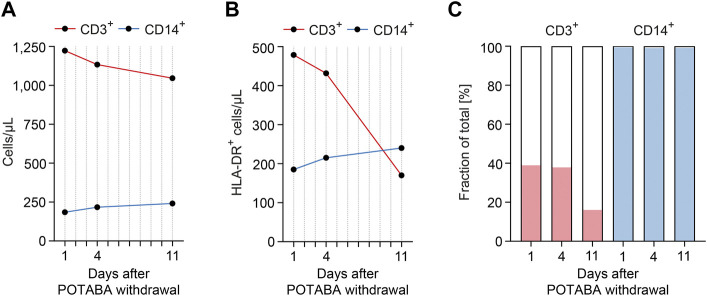
FIGURE 2.
Kinetics of HLA-DR+ T lymphocytes associate with recovery from hepatotoxicity induced by POTABA. (A,B) Monitoring of circulating total and HLA-DR+ monocytes (CD14+ HLA-DR+) and T lymphocytes (CD3+ HLA-DR+) by flow cytometry revealed that improvement of liver injury after POTABA withdrawal resulted in a rapid decline of absolute CD3+ HLA-DR+ T lymphocyte counts, while CD14+ HLA-DR+ monocytes remained unaffected. (C) Fraction of HLA-DR+ cells within the total monocyte (CD14+) and T lymphocyte (CD3+) populations confirm that improvement of liver injury after POTABA withdrawal resulted in a rapid decline of relative CD3+ HLA-DR+ T lymphocyte counts. Abbreviations: HLA-DR, human leukocyte antigen receptor; POTABA, potassium para-aminobenzoate.