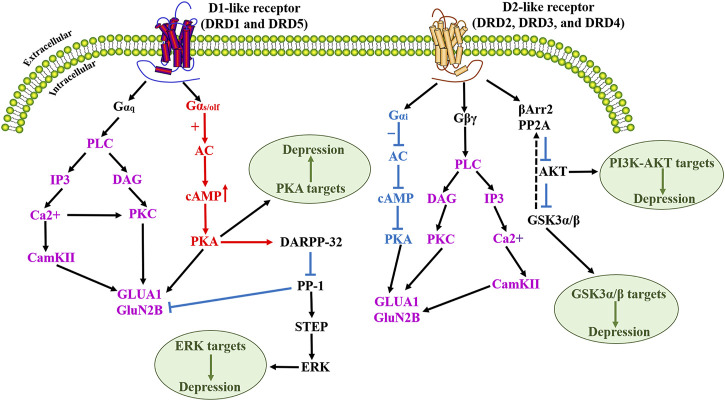
FIGURE 2.
Schematic diagram of D1-like dopamine receptor and D2-like dopamine receptor activation signaling cascade. Upon activation of the dopamine D1-like receptor, activated PKA mediates the phosphorylation of DARPP-32, which acts as an effective inhibitor of PP-1, which in turn dephosphorylates another phosphatase STEP. Dopamine D1-like receptor activation mediates dopamine-dependent inhibitory cascades by increasing ERK phosphorylation by blocking the dephosphorylation of STEP. Numerous studies have demonstrated that modulation of the cAMP/PKA signaling pathway can improve depression. D2-like receptor activation promotes phosphorylation/activation of Akt and phosphorylation/inactivation of its substrate GSK-3β. The physiological significance of this D2 receptor-activated Akt/GSK3 signaling has been extensively discussed in terms of neuroprotection against oxidative stress in depression. In addition, numerous studies have also shown that the PI3K/Akt pathway has an integral role in the treatment of depression. PLC, Phospholipase C; IP3, Inositol triphosphate; CamKII, calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; DAG, diacylglycerol; PKC, protein kinase C; GluA1, glutamate A1; GluN2B, Glutamate Receptor Ionotropic, NMDA 2B; AC, Adenylyl cyclase; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PKA, Protein Kinase A; DARPP-32, Dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein; PP-1, protein phosphatase-1; STEP, striatal-enriched tyrosine phosphatase; ERK, extracellular-signal-regulated kinases; βArr2, β-arrestin-2; PP2A, protein phosphatase 2A; Akt, protein kinase B; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase 3.