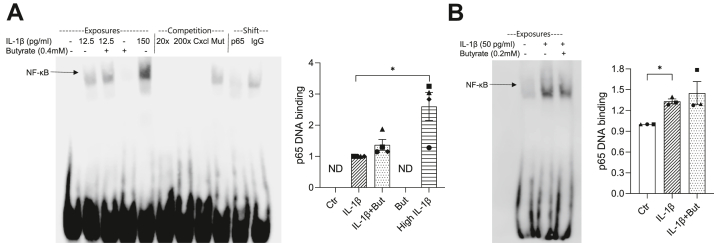
Figure 4.
NF-κB p65 DNA binding activity in INS-1E cells and mouse islets. INS-1E cells (A) or mouse islets (B) were exposed to IL-1β for 1 h with or without 1 h preexposure to butyrate (But) or left unexposed (Ctr). A positive control exposed to 150 pg/ml IL-1β was included. NF-κB p65 DNA binding activity was measured using EMSA. Nuclear extracts were incubated with a probe containing a κB site of the Nos2 promoter. Competition assays were performed with extracts from IL-1β-exposed INS-1E cells using 20 or 200 times excessive nonlabeled probe, a probe with a κB site within the Cxcl1 promoter and a mutated probe (Mut). Supershifts were performed with anti-p65 and IgG antibodies. DNA–protein complexes were resolved on DNA retardation gels. Representative blots are shown. Band intensities were quantified using Image Studio. Data are shown as fold increase relative to IL-1β-exposed cells or Ctr and bars show means ± SEM of n = 3 to 4. ∗p < 0.05. ND, not detectable. EMSA, electrophoretic mobility shift assays; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB.