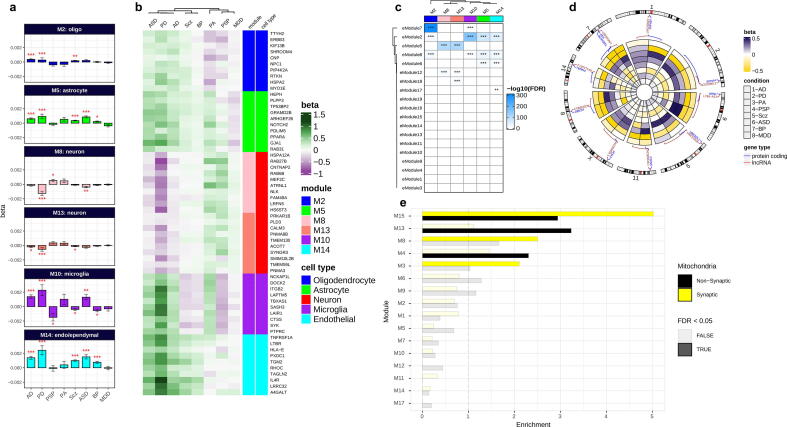
Fig. 5.
Co-expression gene module characterizations. (a) Differential expression of cell-type-specific modules across conditions. β values on the y-axis computed by linear mixed effect model show the relationship of modules eigengenes with conditions. (b) Differential expression of top hub genes within cell-type-specific modules across conditions. Brain cell-type-specific modules are annotated with colors. (c) Enrichment of brain enhancer RNAs for cell-type-specific modules. The overlap between co-expression modules and eRNA modules from an independent dataset [67] was computed by Fisher’s exact test (FDR < 0.05). Color key shows the -log10 (FDR-corrected p-values; *FDR < 0.05, **FDR < 0.01, ***FDR < 0.001; see also Supplementary Fig. S22). (d) A circular heatmap showing expression of protein-coding and their flanking lncRNAs in neuron modules M8 and M13 across conditions (see also Supplementary Fig. S23). (e) The enrichment of co-expression modules for mitochondrial transcriptomes. An independent study that previously reported synaptic and nonsynaptic mitochondria co-expression modules was obtained and compared to co-expression modules in this study using Fisher’s exact tests (FDR < 0.05). Yellow and black colors represent enrichment of synaptic and nonsynaptic mitochondrial transcriptomes for co-expression modules. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)