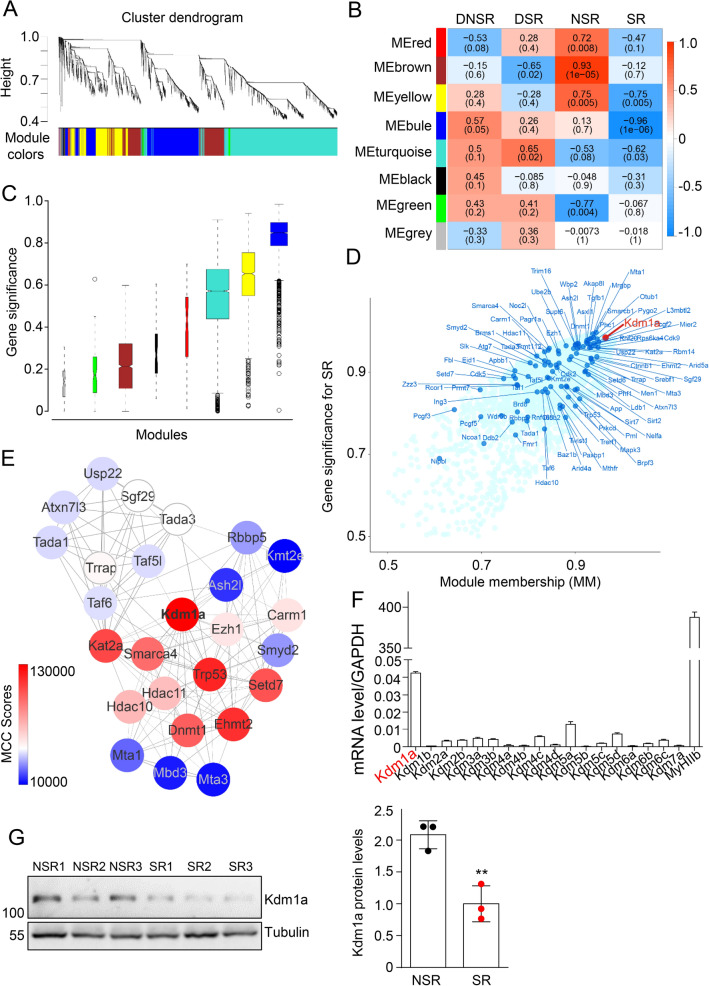
Fig. 6.
WGCNA revealed Kdm1a as a negative regulator of NMJ gene expression. A A total of 11,000 genes expressed in NSR and SR with or without motoneuron innervation were analyzed by WGCNA across 12 samples. According to their expression patterns, genes were clustered as shown by the dendrogram. Clusters of genes showing similar expression profiles are identified as modules and marked by different colors. It could be assigned into eight modules. B Heat-map showed Pearson correlation coefficients and significance levels between modules and different muscle conditions include NSR, SR, DNSR, and DSR. C Box plot showed the gene significance associated with SR in every module. D Genes assigned to the blue module were shown in the scatter plot. Genes related to histone modification were highlighted in navy blue. Module-Membership and gene significance of Kdm1a are 0.98 and 0.96 respectively. E STRING analysis of protein–protein interactions (PPI) from 93 genes related to histone modification in the blue module. The maximal clique centrality (MCC) was used to evaluate the interactome and only genes with MCC score over 10,000 were shown. F Real-time PCR analysis showing the highest expression of Kdm1a among lysine demethylase family members. TA muscles from 3-month-old mice were homogenized and mRNA were extracted for real-time PCR analysis. GAPDH was used as an internal control. MyHIIb was used as a control of muscles. G Immunoblot showing that the higher Kdm1a in NSR than those in SR of diaphragm muscles. n = 3 mice. Right, statics results. Unless otherwise specified, three independent experiments were performed; the mean ± SEM is shown. t-test in **p < 0.01