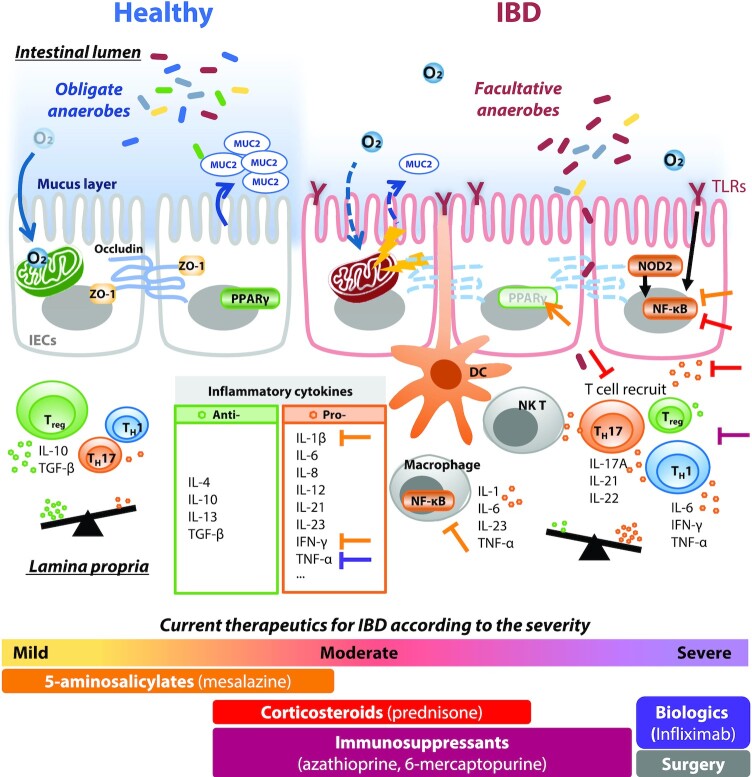
FIGURE 1.
Schematic diagram of healthy compared with impaired gut epithelial mucus layers. Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota with a relatively aerobic intestinal lumen is the cause and/or consequence of IBD. Epithelial barrier integrity is lost in IBD, with decreased mucus layer thickness, low expression of MUC2, and abnormal expression of TJ proteins, including ZO-1 and occludin. Increased epithelial permeability due to loss of barrier function activates inflammatory responses by increasing exposure of intestinal epithelial cells and immune cells to pathogens or antigens. DC, dendritic cell; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; MUC2, mucin 2; NK T, natural killer T cell; NOD2, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 2; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; TH, helper T cell; TLR, toll-like receptor; Treg, regulatory T cell; ZO-1, zonula occludens-1.