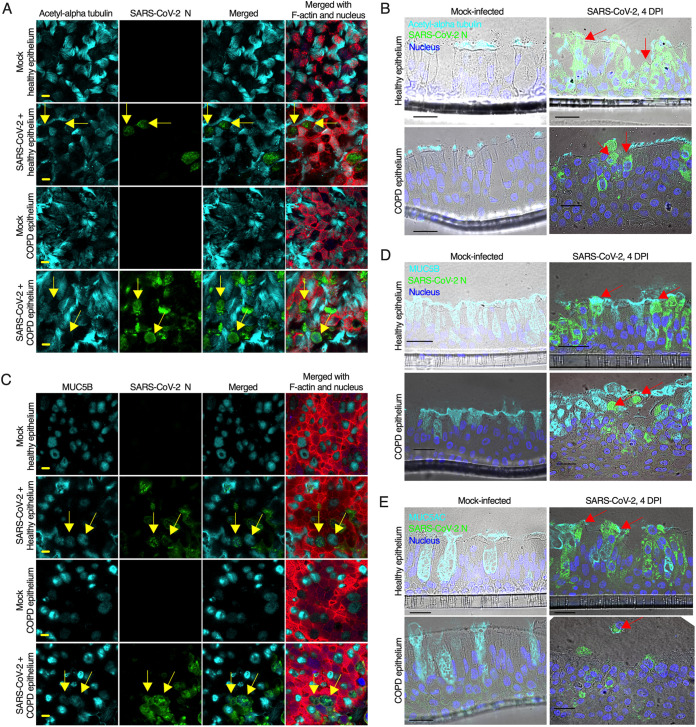
FIG 4.
SARS-CoV-2 infects goblet cells. (A) The airway epithelia were mock-infected or infected with SARS-CoV-2 at an MOI of 0.1. At 4 days postinfection (dpi), the epithelia were fixed, permeabilized, and stained for the identification of cilia (anti-acetyl-alpha tubulin, cyan), SARS-CoV-2 N (anti-N, green), F-actin (rhodamine phalloidin, red), and nuclei (DAPI, blue). The arrows indicate SARS-CoV-2-infected nonciliated cells. (B) At 4 dpi, the epithelia (described in panel A) were stained for the ciliated cell marker acetyl-alpha tubulin (anti-Ac-alpha tubulin, cyan), SARS-CoV-2 N (anti-N, green), and F-actin (rhodamine phalloidin, red); the nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). The arrows indicate nonciliated infected cells. (C) At 4 dpi, the epithelia (described in panel A) were embedded in paraffin, sectioned, and stained for the detection of MUC5B-positive goblet cells (anti-MUC5B, cyan) and SARS-CoV-2 N (anti-N, green); the nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). The arrows indicate SARS-CoV-2-infected nonciliated MUC5B-positive goblet cells. (D) At 4 dpi, the sectioned epithelia were stained for the goblet cell marker MUC5B (anti-MUCB, cyan) and SARS-CoV-2 N (anti-N, green); the nuclei were also stained with DAPI (blue). The arrows indicate SARS-CoV-2-infected MUC5B-positive goblet cells. (E) At 4 dpi, the sectioned epithelia were stained for the goblet cell marker MUC5AC (anti-MUC5AC, cyan) and SARS-CoV-2 N (anti-N, green); the nuclei were also stained with DAPI (blue). The arrows indicate SARS-CoV-2-infected MUC5AC-positive goblet cells. (A and B) Bar = 5 μm. (C, D, and E) Bar = 20 μm. See also Fig. S3 and S4.