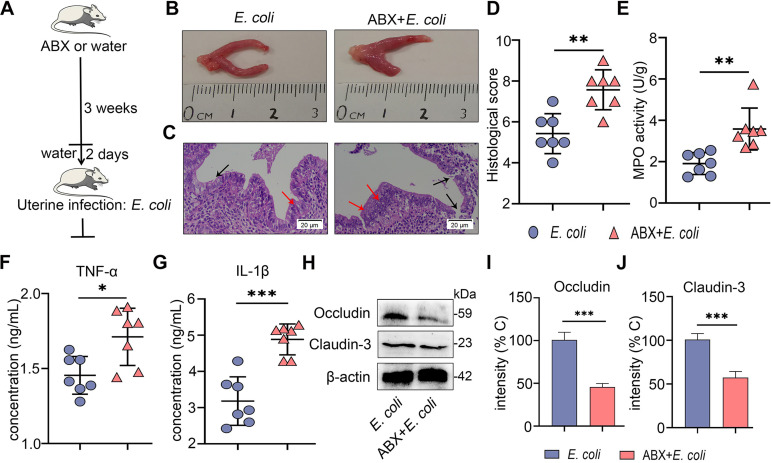
FIG 4.
Gut dysbiosis aggravates E. coli-induced endometritis in mice. (A) A schematic representation is shown. Mice were treated with ABX (1 g/L ampicillin, metronidazole, and neomycin sulfate and 0.5 g/L vancomycin) for 3 weeks followed by E. coli administration, and uterine samples were harvested for assessment 24 h after E. coli treatment. (B-C) Representative macroscopic images (B) and H&E-stained uterine sections (C) are shown. The red arrow shows inflammatory changes (immune cell infiltration or tissue proliferation). The black arrow indicates endometrial damage (scale bar = 20 μm). (D-G) Histological score (D), MPO activity (E), and inflammatory cytokines TNF-α (F) and IL-1β (G) were determined from different treatment groups (n = 7). (H) Uterine occludin and claudin-3 protein expressions were assessed by Western blotting from indicated mice. Intensity analysis of occludin (I) and claudin-3 (J) was performed based on Western blotting (n = 7). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD, and two-tailed Student's t test was performed for statistical analysis (D-G and I-J). *, P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001 indicate significant differences.