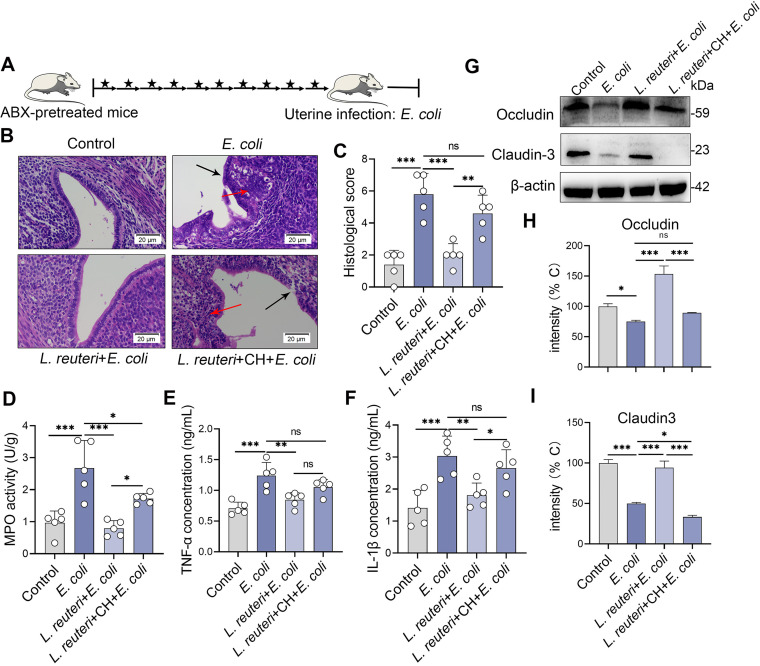
FIG 8.
The protective effects of L. reuteri on E. coli-induced endometritis depend on the activation of AhR in mice. (A) Schematic representation of L. reuteri and CH223191 treatment is shown. Mice were treated with CH223191 (500 μg/kg BW) intraperitoneally after each oral gavage of L. reuteri (109 CFU/300 μL). The arrow indicates L. reuteri supplementation and the star indicates CH223191 treatment. On day 21, mice were treated with E. coli (108 CFU/30 μL) to induce endometritis. (B) Representative H&E-stained uterine images are shown. (C-F) Histological scores (C), MPO activity (D), and TNF-α (E) and IL-1β (F) levels were determined from different treatment groups (n = 5). (G) Levels of uterine occludin and claudin-3 from the indicated mice were assessed by Western blotting. Intensity analysis of occludin (H) and claudin-3 (I) was performed based on Western blotting (n = 5). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD, and one-way ANOVA was performed for statistical analysis (C-F and H-I). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001 indicate significant differences. ns, no significance. CH, CH223191.