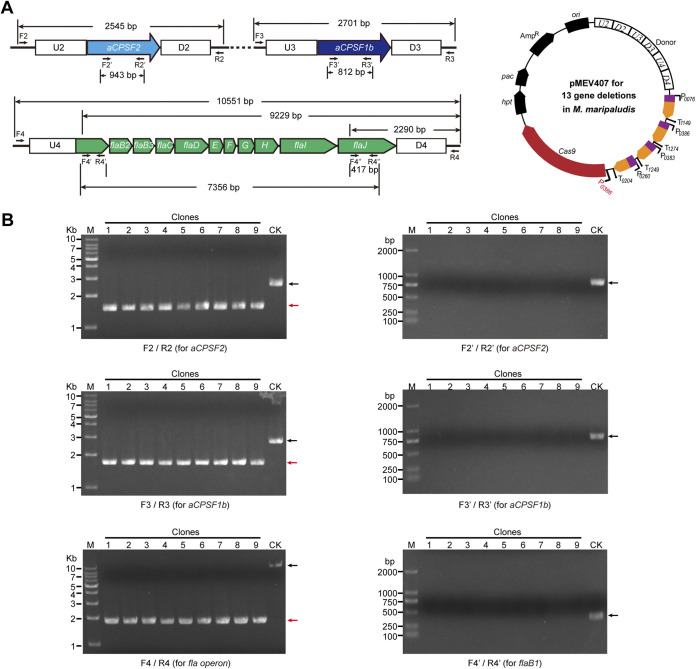
FIG 4.
Synchronous deletion of multiple (13) genes substituted in three genomic loci in M. maripaludis using the Cas9 editing system. (A) Schematic of the plasmid designed for the synchronous deletion of 13 genes consisting of the fla operon genes (MMP1666 to MMP1676) and aCPSF2 (MMP0431) and aCPSF1b (MMP1381). Plasmid pMEV407 encodes four sgRNAs that match aCPSF2, aCPSF1b, flaB1 (MMP1666), and flaJ (MMP1676) (right). They were expressed under the control of the indicated promoters, which were derived from the highly expressed genes in M. maripaludis. The sequences upstream (U2, U3, and U4) and downstream (D2, D3, and D4) of each gene were concatenated on pMEV407 to provide the recombinant donor. Distinctly, the Cas9 in pMEV407 was expressed under the control of promoter P0386 from the highly expressed gene MMP0386. (B) Nine puromycin-resistant transformants were randomly selected and subjected to PCR assay. Primer pairs F2/R2, F2′/R2′, F3/R3, F3′/R3′, F4/R4, and F4′/R4′ were used to detect the knockout of aCPSF2, aCPSF1b, and the fla operon genes, respectively. Black and red arrows indicate the PCR products amplified from the wild-type (lane CK) and the mutated genomes (lanes 1-9), respectively. M, dsDNA size marker.