FIG 6.
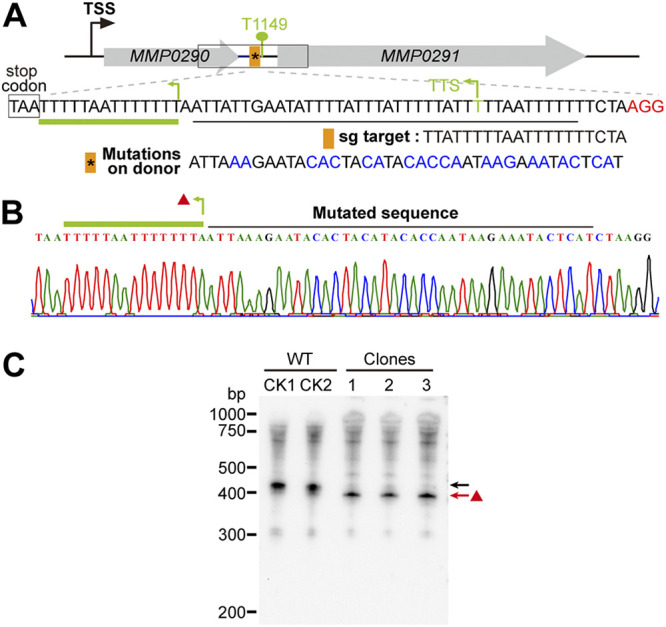
Cas9-based in situ multinucleotide mutagenesis to determine the key residues in a terminator of M. maripaludis. (A) Design schematic showing the in situ mutagenesis of multiple nucleotides in a terminator identified by Term-seq previously (33, 34). An sgRNA that targets the terminator region (orange bar with the asterisk indicating the nucleotide mutation) was expressed, and the multiple nucleotides in blue letters that were designed to replace the U-rich sequence of the terminator were introduced into the donor sequence at the pMEV4 plasmids. The PAM sequence is shown in red letters. TSS, transcription start site. (B) Five randomly selected transformants were screened via PCR using the primers F7/R7 depicted in panel A. Nucleotide mutations were further validated by DNA sequencing. The red triangle indicates a U-rich sequence present upstream, a potential new terminator of MMP0290. (C) Northern blotting detected the transcript of MMP0290 in the wild-type (WT) (black arrow) and the multinucleotide-mutated transformants (clones 1-3) (red arrow) on the primary terminator. The red arrow points to a short transcript detected in the terminator mutants, which appeared to terminate at the upstream uridine-rich terminator sequence (green bent arrow in panel B).
