FIG 2.
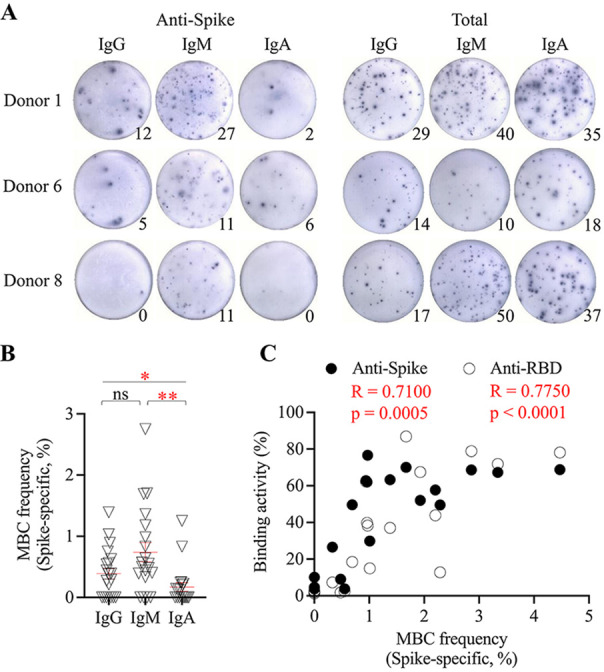
Anti-spike memory B cell response to natural infection with SARS-CoV-2. (A) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot showing SARS-CoV-2 spike-specific IgG, IgM, and IgA memory B cell in the peripheral blood upon natural infection. Circulating total IgG, IgM, and IgA memory B cells were also measured. A total of 200,000 cultured cells were added into each of the anti-spike B cell wells, and 5,000 cultured cells were added into each of the total B cell wells. Donor 1 (day 27) was a 55-year-old woman with severe COVID-19 with pneumonia. Donor 6 (day 21) was a 43-year-old man with moderate COVID-19 and pneumonia. Donor 8 (day 18) was a 22-year-old woman with mild COVID-19 and a running nose. (B) Frequency of spike-specific IgG, IgM, and IgA memory B cells in the peripheral blood (n = 20). The frequency is defined as the percentage of spike-specific IgG (IgM or IgA) B cells in the total IgG (IgM or IgA) B cells. Each point represents memory B cell frequency for each patient, and the red line represents mean ± standard error of mean. One-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s test was used to compare the difference among groups. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. ns, not significant. (C) Relationship of spike-specific memory B cell frequency (IgG + IgM + IgA) and spike-binding and RBD-binding serological activity among COVID-19 patients. Linear regression was used to model the relationship between two variables. MBC, memory B cell.
