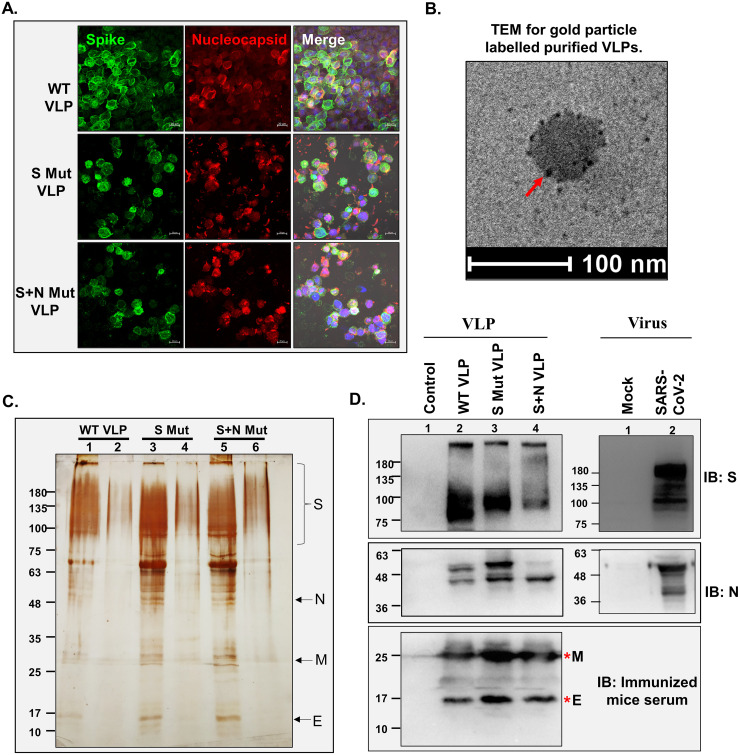
FIG 2.
Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 VLPs. (A) Expression of SARS-CoV-2 proteins in Sf21 cells. Baculovirus-infected Sf21 cells were harvested after 96 h and processed for confocal staining using anti-S- and anti-N-specific primary antibodies and Alexa Fluor 488 (AF488)- and AF633-labeled secondary antibodies. Nuclei were counterstained using DAPI. Bar, 20 μm. (B) Transmission electron microscope images of purified VLPs. The purified VLPs were fixed, added to the copper grid, and stained for S protein using specific primary and immunogold-labeled secondary antibody. Negative staining was done using uranyl oxalate. The arrow indicates immunogold-labeled S protein. (C) The purified VLPs were loaded onto SDS–10% polyacrylamide gels, followed by silver staining (adjacent to the VLP lane, a lower fraction of the gradient was loaded, confirming the VLP purity). Lanes 1, 3, and 5 represent purified VLP lanes. (D) Western blot to detect the presence of S protein and N protein using specific primary antibodies and HRP-tagged secondary antibodies for purified VLPs and SARS-CoV-2-infected cell lysate. Sera from VLP-injected mice was used as primary antibody, followed by HRP-tagged anti-mouse antibody as secondary antibody for detecting M protein and E protein.