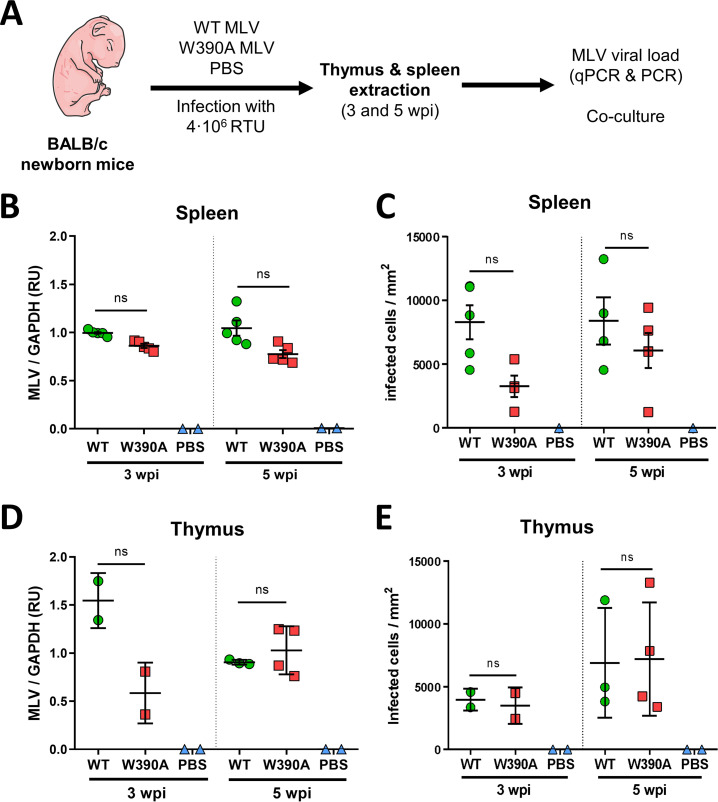
FIG 1.
In vivo replication of WT MLV and W390A MLV in murine tissue. (A) Schematic representation of the workflow to evaluate the in vivo infectivity of WT MLV and W390A MLV. Newborn mice were infected by intraperitoneal injection with 4 × 105 RTU of WT MLV or W390A MLV 1 day after birth. Blood was drawn between 80 and 90 days after injection. Extracts of the spleen and thymus were made at 3 and 5 weeks postinfection. (B) MLV loads in spleen cells from mice infected with WT MLV (n = 5) or W390A MLV (n = 5) or injected with PBS (n = 2) at 3 and 5 weeks postinfection. The viral load was measured by RT-qPCR of MLV IN relative to GAPDH levels and represented as relative units (RU). (C) Number of infected NIH 3T3 cells after 1 day of coculture with cells from spleens of mice infected with WT MLV (n = 4) or W390A MLV (n = 4) or injected with PBS (n = 2) at 3 and 5 weeks postinfection. (D) MLV loads in thymus cells from mice infected with WT MLV (3 wpi, n = 2; 5 wpi, n = 3) or W390A MLV (3 wpi, n = 2; 5 wpi, n = 4) or injected with PBS (n = 2) at 3 and 5 weeks postinfection. The viral load was measured by RT-qPCR of MLV IN relative to GAPDH levels. (E) Number of infected NIH 3T3 cells after 1 day of coculture with cells from spleens of mice infected with WT MLV (3 wpi, n = 2; 5 wpi, n = 3) or W390A MLV (3 wpi, n = 2; 5 wpi, n = 4) or injected with PBS (n = 2) at 3 and 5 weeks postinfection. No statistically significant difference was found using a Kruskal-Wallis test (B to E). ns, not significant.