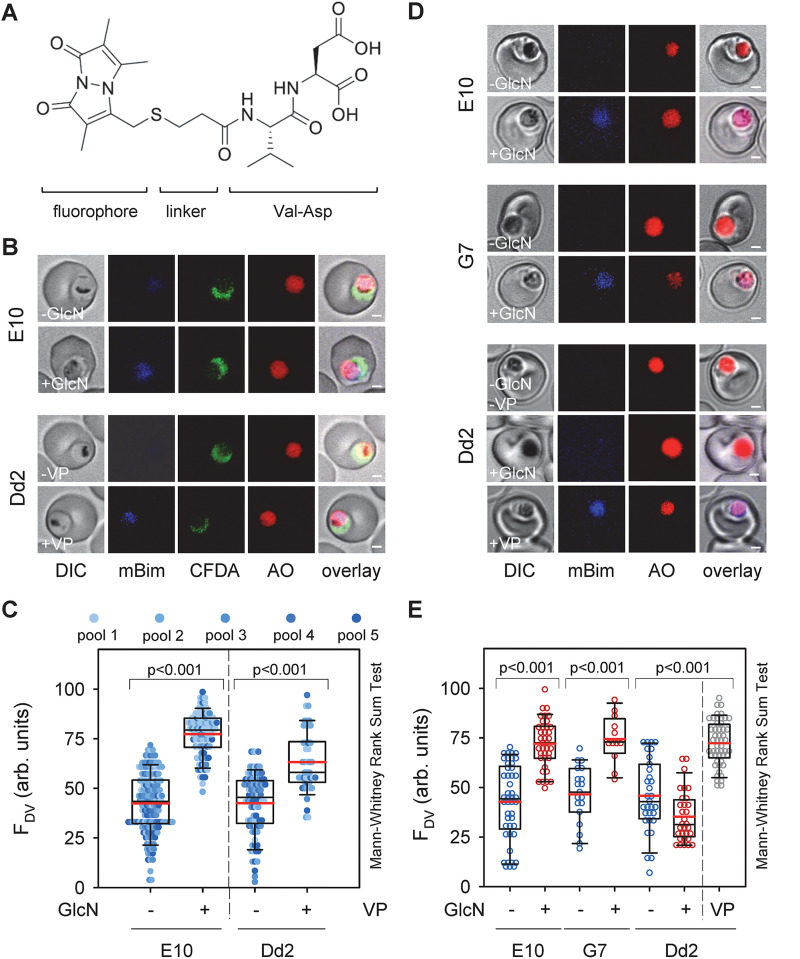
FIG 6.
Accumulation of fluorescently labeled dipeptides in the digestive vacuole of PfCRT knock-down mutants under induced conditions. (A) Chemical structure of a representative fluorescently labeled di-peptide, consisting of the fluorophore monobimane, the linker 3-mercaptopropionic acid, and the amino acids valine and aspartic acid. (B) Representative live cell confocal fluorescence images showing accumulation of fluorescently labeled di-peptides (pool 1; mBim) in the digestive vacuole of the PfCRT knock-down mutant E10 under induced (+GlcN; 1 mM for 3 day) and non-induced (-GlcN) conditions and in Dd2 in the presence (+0.89 μM VP for 3 day) and absence of verapamil (-VP), a partial mixed type inhibitor of PfCRTDd2 (35). Acridine orange (AO) and 5-carboxyfluorescein diacetate (cFDA) were used as live cell viability probes staining the digestive vacuole and the parasite’s cytoplasm, respectively. Bar, 1 μm. (C) Quantitative analysis of fluorescence signal associated with dipeptides in the digestive vacuole (FDV) of the PfCRT knock-down mutant E10 under induced and non-induced conditions and Dd2 in the presence and absence of verapamil. The pools contained the following fluorescently labeled dipeptides: pool 1: KT, AQ, HL, NL, LS; pool 2: GS, LT, PA, SP, GV, VD; pool 3: PK, GH, PV, LP, DK; pool 4: KS, HK, MP, KG, SH, HL; pool 5: QA, LH, SL, TL, GV, SV (Table S9). (D) Like B with the exception that the fluorescently labeled dipeptide VD was investigated. Bar, 1 μm. (E) Like B with the exception that the fluorescently labeled dipeptide VD was investigated.