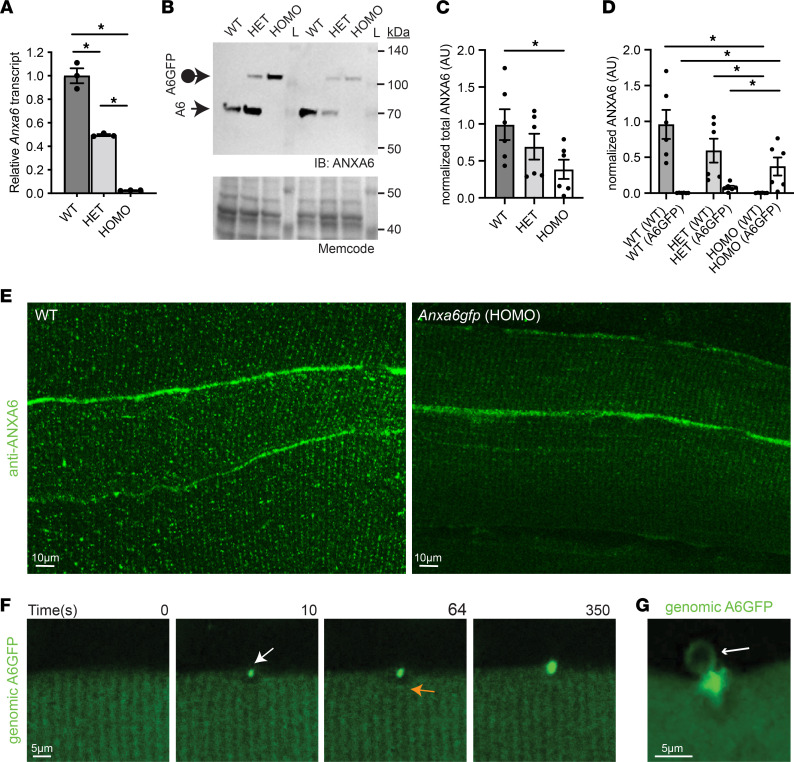
Figure 2. Genomic A6GFP protein localizes to the site of muscle membrane injury.
(A) Quantitative PCR demonstrates reduced Anxa6 levels in quadriceps from heterozygous and homozygous Anxa6gfp mice compared with wild-type (WT) controls. (B–D) Anti–annexin A6 immunoblots demonstrate reduced ANXA6 protein levels in quadriceps muscles from heterozygous and homozygous Anxa6gfp mice. The loading control is a 42 kDa band detected by MemCode reversible protein stain. (E) Anti–annexin A6 (shown in green) immunofluorescence imaging of extensor digitorum longus myofibers from WT and homozygous Anxa6gfp mice. ANXA6 and annexin A6GFP protein localize in a similar punctate, sarcomeric pattern and at the sarcolemma. Scale bar: 10 μm. (F) Upon laser-induced membrane injury, annexin A6GFP localized to the repair cap (white arrow) with a visible clearance zone (orange arrow) beneath the membrane lesion in heterozygous Anxa6gfp myofibers. (G) Genomically encoded annexin A6GFP membranous blebs (white arrow) erupt from the site of membrane injury. Z-stack images from an injured myofiber. Scale bar: 5 μm. n = 6 mice per genotype. n > 10 myofibers. *P < 0.05 by 1-way ANOVA.