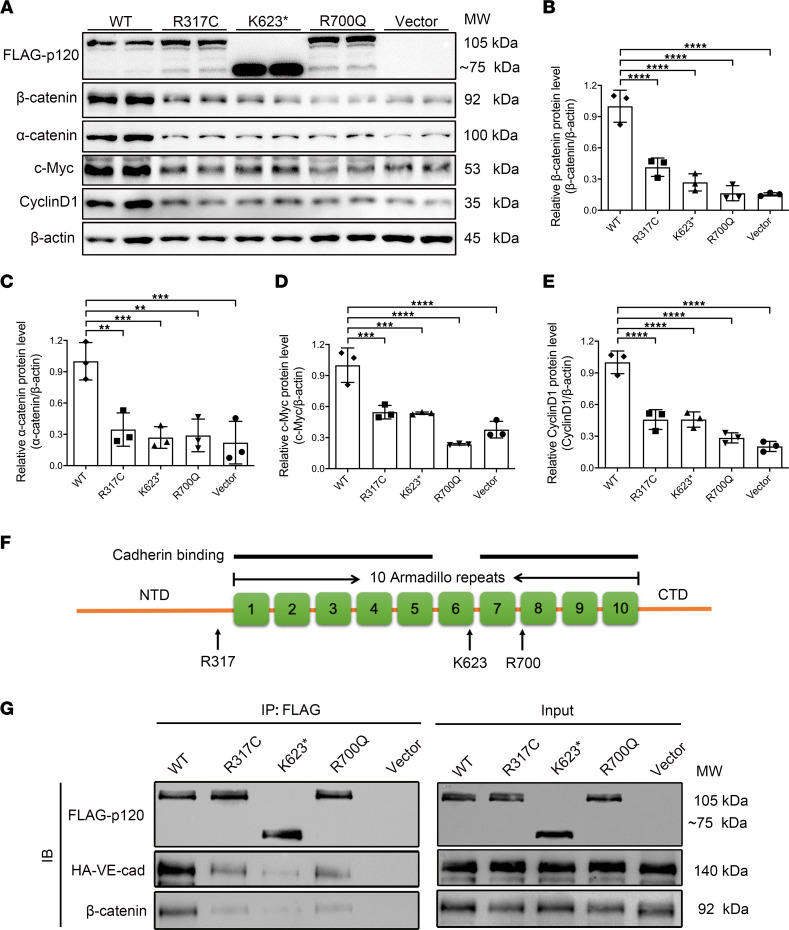
Figure 9. Functional consequences of CTNND1 variant alleles.
(A) Western blot analysis of protein levels of overexpressed FLAG-p120 and endogenous β-catenin, α-catenin, c-Myc, and CyclinD1 in HEK293T cells transfected with wild-type (WT), variant, or vector plasmids. (B–E) Quantification of relative protein levels of endogenous β-catenin, α-catenin, c-Myc, and CyclinD1 in HEK293T cells transfected with WT, variant, or vector plasmids. The P values are from multiple comparisons in 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (n = 3); **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. (F) Schematic diagram of p120 protein. p120 consists of 10 armadillo repeat (ARM) domains flanked by N-terminal (NTD) and C-terminal (CTD) domains. The potential binding surfaces for cadherins are indicated with black lines. The locations of mutated residues are indicated with black arrows. (G) Western blot analysis of FLAG-p120 (WT, variant, or vector) co-immunoprecipitated with HA-VE-cadherin (HA-VE-cad) or endogenous β-catenin. An empty vector was used as negative control. Experiments were performed at least 3 times independently.