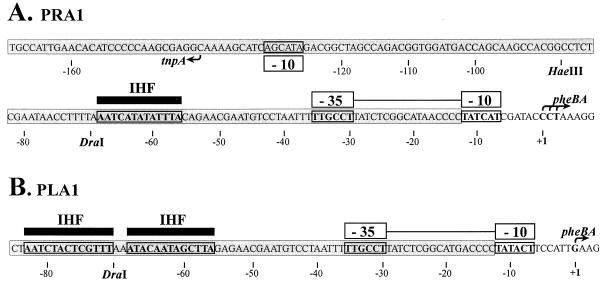
FIG. 1.
Nucleotide sequence of the fusion promoters PRA1 (A) and PLA1 (B). Fusions between −35 hexamer provided by the inverted repeats of Tn4652 and −10 hexamers found in the target DNA upstream of the pheBA genes created these promoters (36). The sequences of Tn4652 are shaded. Locations of −10 and −35 hexamers of the fusion promoters are indicated above the sequence. The upstream region of the promoter PRA1 overlaps with the oppositely directed promoter region of the Tn4652 transposase gene tnpA. Location of −10 hexamer of the tnpA promoter is shown below the sequence of the right end of Tn4652. Transcription start sites for the promoters, determined by primer extension experiments, are indicated by arrows. The potential IHF binding sites at the ends of Tn4652 resembling the E. coli IHF binding consensus sequence WATCAANNNNTTR are indicated above the sequences of the promoters PRA1 and PLA1 by black bars. Restriction sites relevant to the experiments presented in this paper are shown.