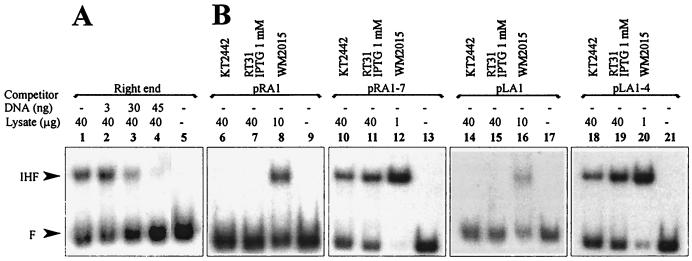
FIG. 5.
(A) Gel shift assay demonstrating suppression of the formation of the P. putida IHF complex with the right end of Tn4652 by nonlabeled DNA fragment containing Pu promoter region. Cell lysates used were from P. putida KT2442. (B) Gel shift assay of in vitro binding of P. putida and E. coli IHF to the ends of Tn4652 lacking A-T-rich regions upstream of the IHF binding core sequence (DNA probes from plasmids pRA1 and pLA1) and in the presence of A-T-rich regions (DNA probes from plasmids pRA1-7 and pLA1-4). Lysates used were from E. coli WM2015 (lanes 8, 12, 16, and 20) and P. putida KT2442 (lanes 6, 10, 14, and 18) and RT31 grown in the presence of 1 mM IPTG (lanes 7, 11, 15, and 19). No cell lysate was added to the reaction mixture in lanes 9, 13, 17, or 21. All lysates were prepared from stationary-phase cells.