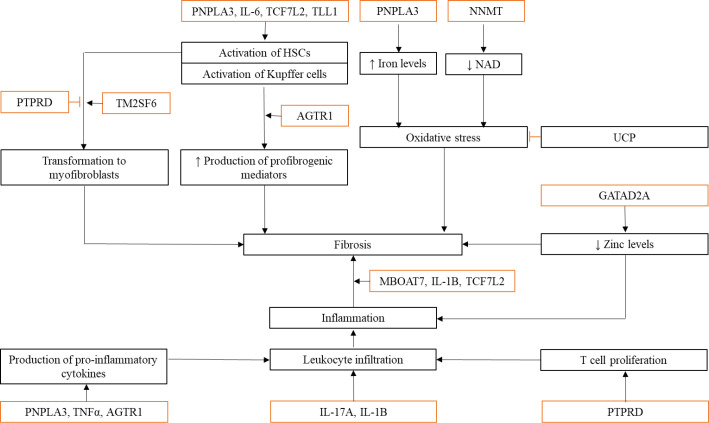
Fig. 3.
NAFLD-associated SNPs involved in liver inflammation and fibrosis. Inflammation is a contributing factor in fibrogenesis. Changes in genes involved in both processes can affect the development and progression of NAFLD. Mutations in PTPRD, PNPLA3, TNF-α, AGTR1, IL-17A, IL-1B, and GATAD2A indirectly cause fibrosis by inducing inflammatory responses through increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, increased immune cell proliferation, and leukocyte recruitment. Other polymorphisms are involved in fibrogenesis by either activating HSCs and Kupffer cells or inducing oxidative stress in liver tissue. Activated HSCs can transform into myofibroblasts that will then produce excess collagen, resulting in tissue scarring. (→: promote; ─|: inhibit; : mutated genes; ↓: decreased; ↑: increased)