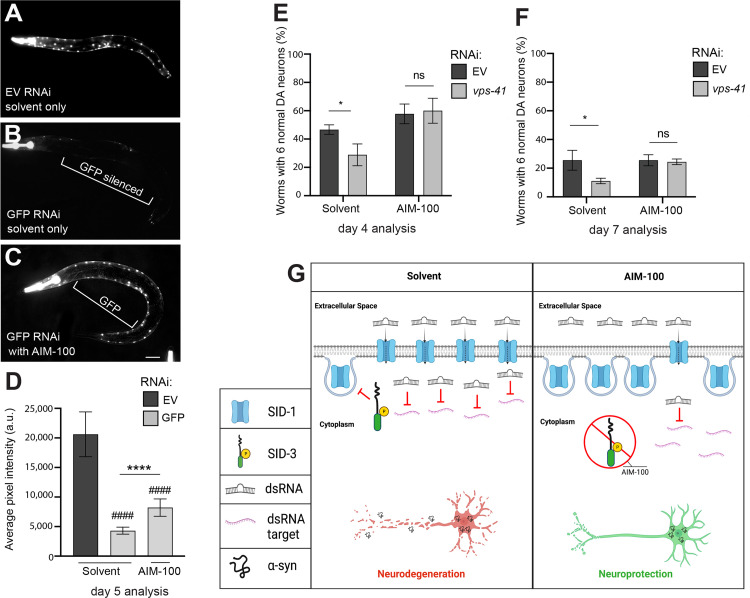
Fig 2. AIM-100 reduces dsRNA silencing in body wall muscle and decreases DA neurodegeneration.
(A-D) AIM-100 diminishes RNAi silencing in body wall muscle cells. RNAi in representative worms overexpressing GFP in body wall muscle cells, with and without the SID-3 inhibitor AIM-100 (100 μM) in 0.1% ethanol solvent. Worms were tested on day 5 post-hatching. (A) Empty vector (EV) RNAi in worms overexpressing GFP in body wall muscle cells exposed to the solvent. (B) GFP RNAi in worms overexpressing GFP in body wall muscle cells exposed to the solvent. (C) GFP RNAi in worms overexpressing GFP in body wall muscle cells and administered AIM-100. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Average pixel intensity was measured at day 5 post-hatching in worms in the same conditions outlined in (A-C). Values represent mean + S.D. (n = 30 worms per group per replicate, 3 independent replicates). Two-Way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis was used to compare all groups to each other; Symbols above bars are in comparison to the solvent group with EV RNAi; #### P < 0.0001. Symbols above brackets are in comparison to bars indicated. **** P < 0.0001. (E, F) DA neurodegeneration levels in an RNAi-sensitive α-syn model background designed to allow knockdown of genes solely in DA neurons (strain UA196) and analyzed at days 4 and 7 post-hatching. Worms were either exposed to the 0.1% ethanol solvent control or AIM-100 (100 μM), and within each of these conditions, mock RNAi (empty vector) or vps-41 (positive control) RNAi was performed. Values represent mean + S.D. (n = 30 worms per genotype per replicate, 3 independent replicates). Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis was used to compare all conditions to each other; ns P ≥ 0.05, * P < 0.05. Values represent mean + S.D. (n = 30 worms per genotype per replicate, 3 independent replicates). (G) An illustration (created with Biorender.com) depicting model scenarios for the import of dsRNA (targeting vps-41, an established control for DA neurodegeneration when knocked down) into DA neurons via SID-1 in transgenic animals expressing α-syn, either in the presence (left pane) or absence (right pane) of treatment with the selective inhibitor of SID-3 activity, AIM-100. The left pane represents SID-3 actively blocking the endocytosis of SID-1 in the absence of AIM-100 (solvent only), therefore maintaining dsRNA transport for the silencing of target genes, such as vps-41, which enhances DA neurodegeneration when knocked down. In contrast, the right pane displays a scenario that explains the observed inhibition of SID-3 by AIM-100 treatment seen when α-syn is expressed in DA neurons; in this scenario AIM-100 reduces the activity of SID-3 and allows for endocytosis of SID-1, thereby resulting in less SID-1 on cell surfaces and reduced dsRNA import into cells. This leads to the stability of endogenous vps-41 transcripts and enhanced resistance to α-syn-induced neurodegeneration observed, in accordance with the established function of VPS-41.