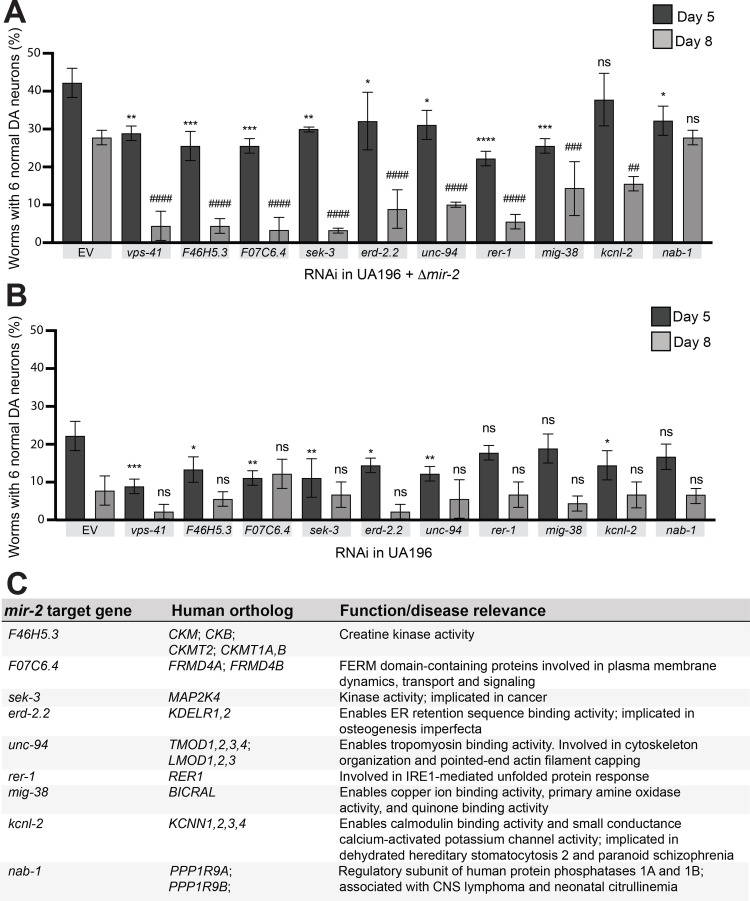
Fig 4. Modulating mir-2-dependent suppression of target gene expression levels alters α-syn-induced DA neurodegeneration.
(A, B) DA neurons were scored for degeneration on days 5 and 8 post-hatching. RNAi was performed in a RNAi sensitive α-syn model with a mir-2(gk259) mutant background (A) and in the RNAi sensitive α-syn model that is mir-2 wildtype (B). Nine validated targets of mir-2 that have human orthologs were knocked down, along with a positive control, vps-41. Values represent mean + S.D. (n = 30 worms per genotype per replicate, 3 independent replicates). One-Way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc analysis was used to compare RNAi knockdowns to empty vector (EV) controls at day 5 and 8 post-hatching. For day 5 analyses, asterisks (*) above bars indicate comparisons of each individual knockdown to EV; ns P ≥ 0.05, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P <0.001, **** P < 0.0001. For day 8 analyses, pound signs (#) above bars indicate comparisons to EV; ns P ≥ 0.05, ## P < 0.01, ### P <0.001, #### P < 0.0001. (C) A list of the nine targets knocked down via RNAi in (A) and (B), their human orthologs, and function.