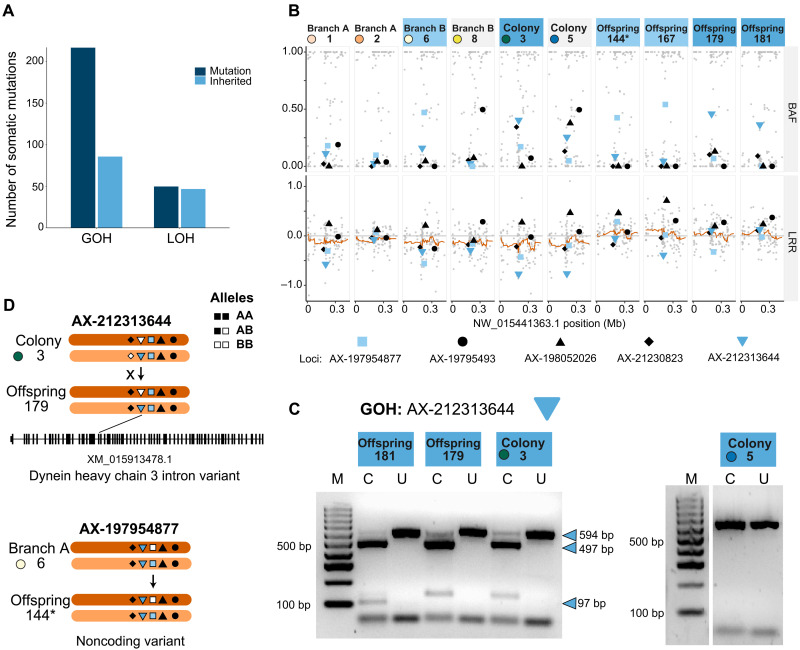
Fig. 2. Characterization and validation of parental somatic mutations inherited by uniparental coral offspring.
(A) Bar plot showing the number of total mutations (dark blue bars) categorized as a GOH or LOH, and the number of mutations in each category that were passed on to offspring (light blue bars). GOH mutations outnumbered LOH mutations, but a greater proportion of LOH mutations were inherited by offspring. (B) Plots of two metrics used to investigate somatic mutations: BAF (B allele frequency; top row) and LRR (log R ratios; bottom row). The orange line represents the 20-bp sliding average of LRR along the scaffold (position in megabases). Blue and black symbols represent specific mutations. Black shapes: not inherited; blue shapes: inherited. Above each plot, adult coral colonies are labeled as in Fig. 1A and juveniles are denoted as “Offspring”. Sample labels are filled according to specific, shared mutations (light blue, locus AX-197954877; medium blue, locus AX-212313644). Samples without those mutations have a white label fill. (C) RFLP validation of inherited GOH mutation AX-212313644. For each sample, the uncut (U) and cut (C) polymerase chain reaction products are shown next to a size standard (lane M). The two offspring (179 and 181) both share the heterozygous mutation also detected in colony 3, resulting in three bands, while colony 5, predicted to have the nonmutant homozygous state for this site, produced only one uncut band. (D) Schematic of inheritance of somatic mutations. RFLP-validated somatic mutation AX-212313644 (down triangle) is found within the intron of the dynein heavy chain 3. GOH mutation AX-197954877 (square) is found on the same scaffold. Symbols represent the five mutations detected along this scaffold in at least one sample in (B). Filled shapes, A allele; open shapes, B allele. Arrows denote inheritance and crosses denote lack of inheritance. Offspring 144 was parthenogenetic (denoted by an asterisk).