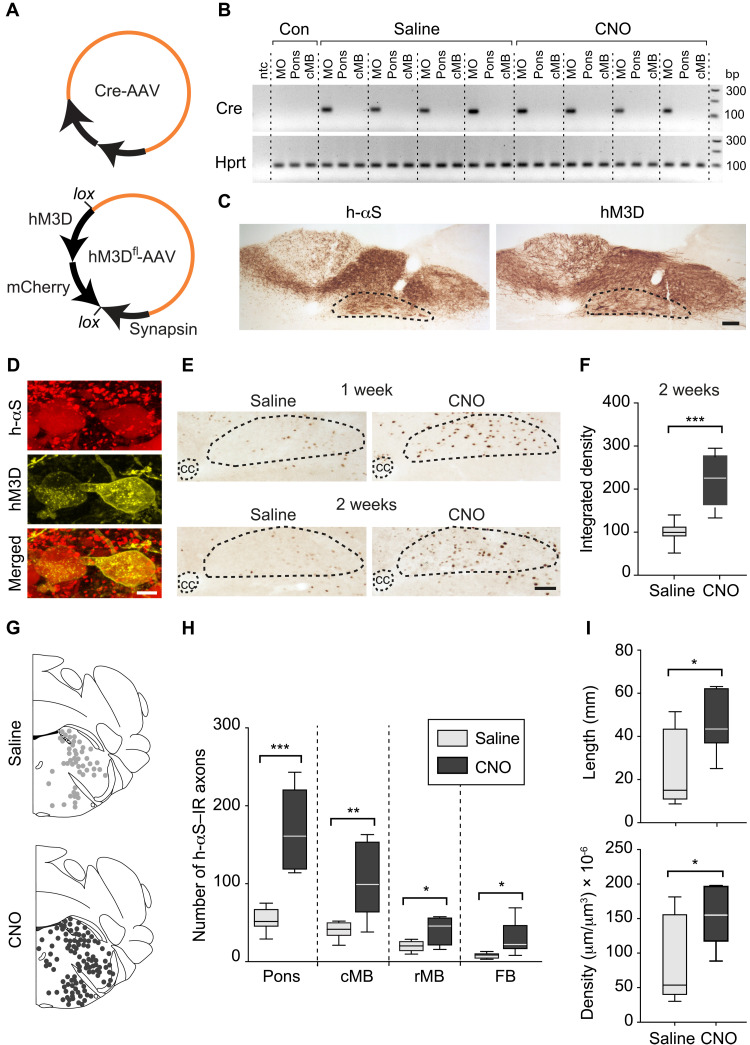
Fig. 3. Neuronal hyperactivity exacerbates caudo-rostral h-αS spreading.
(A and B) Mice were coinjected with Cre-AAVs together with AAVs designed for conditional hM3D DREADD expression (hM3Dfl-AAVs) (A). They also received saline or CNO for 2 weeks (weeks 4 and 5) before sacrifice. Tissue specimens from the left dorsal MO, pons, and caudal midbrain were processed for RT-PCR; specific bands at 116 (Cre) and 90 (Hprt) bp; control samples (Con) from untreated mice; nontemplate control (ntc) (B). (C and D) Mice were coinjected with Cre- and hM3Dfl-AAVs and treated with saline as above. Medullary sections were immunostained with anti–h-αS or anti-RFP; the DMnX is delineated. Scale bar, 100 μm (C). Confocal images of DMnX neurons double-labeled with anti–h-αS and anti-RFP. Scale bar, 10 μm (D). (E and F) Mice received an injection of Cre- and hM3Dfl-AAVs and were treated with saline or CNO for 1 or 2 weeks. Medullary sections were labeled with anti–c-fos; the central canal (cc) and DMnX are delineated. Scale bar, 100 μm (E). Density measurements of c-fos immunoreactivity in the DMnX of mice injected with Cre- and hM3Dfl-AAVs and treated with saline or CNO (n = 8 per group); data were calculated as percentage of the mean value in the saline group (F). (G to I) Mice received an injection of Cre- and hM3Dfl-AAVs and were treated with saline (n = 6, gray) or CNO (n = 7, black). Brain sections were immunostained with anti–h-αS. Schematic plots of the distribution of h-αS–immunoreactive axons in left pontine sections (G). The number of h-αS–immunoreactive axons was counted in the left pons, caudal and rostral midbrain, and forebrain (H). The length and density of h-αS–immunoreactive axons were measured in pontine sections (I). Plots show median, upper and lower quartiles, and maximum and minimum as whiskers. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.