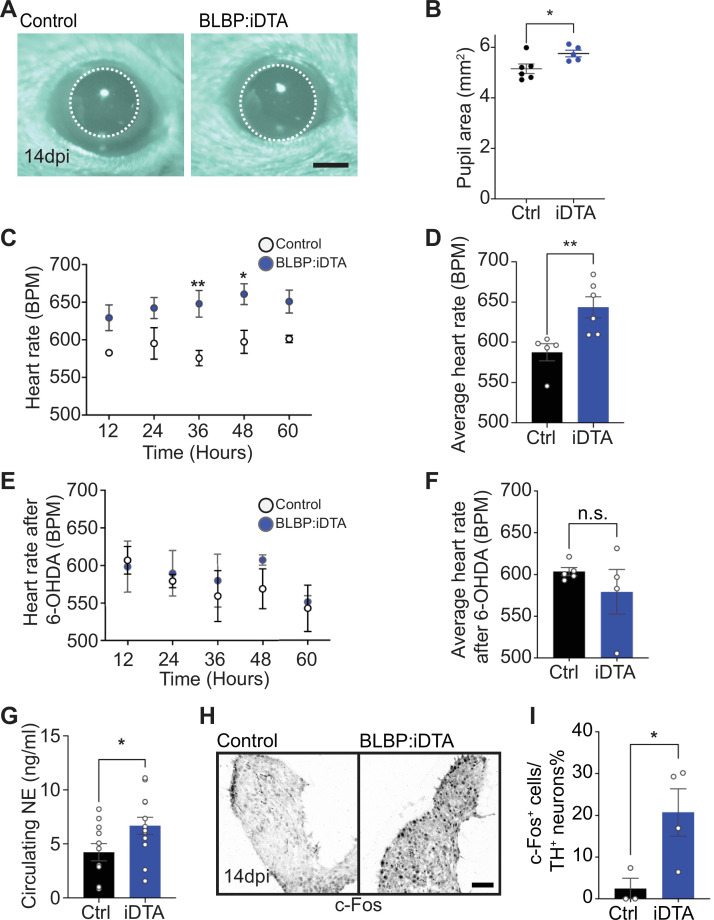
Figure 3. Elevated sympathetic activity in satellite glia-depleted mice.
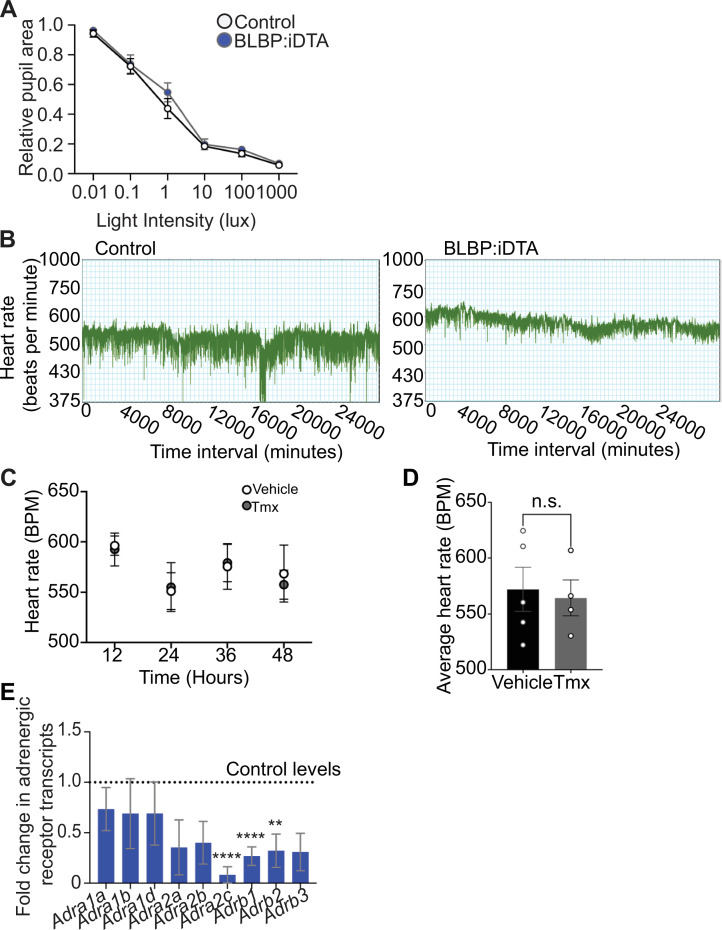
(A, B) Dark-adapted BLBP:iDTA mice have increased basal pupil size compared to control littermates. Results are presented as mean ± SEM from n = 6 control and 5 mutant animals. *p<0.05, t-test. (C) BLBP:iDTA mice exhibit elevated heart rate, relative to controls. ECGs were recorded continuously in conscious mice for 7 days, although only data for fourth to seventh days after insertion of lead implants are included in the analysis. Results are presented as mean ± SEM from n = 5 control and 6 mutant animals. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction. (D) Average heart rate over fourth to seventh days after lead implantation. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 5 control and 6 mutant animals. **p<0.01, t-test. (E, F) 6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) administration (150 mg/kg, i.p.) prevents elevated heart rate in BLBP:iDTA mice. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 5 control and 4 mutant animals, n.s, not significant, t-test. (G) Increased circulating norepinephrine levels in BLBP:iDTA mice. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 11 control and 13 mutant animals. *p<0.05, t-test. (H, I) Increased c-Fos-positive sympathetic neurons in mutant ganglia. Quantification of c-Fos+;TH+ sympathetic neurons as a % of total number of TH+ sympathetic neurons. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 3 control and 4 mutant animals. *p<0.05, t-test.