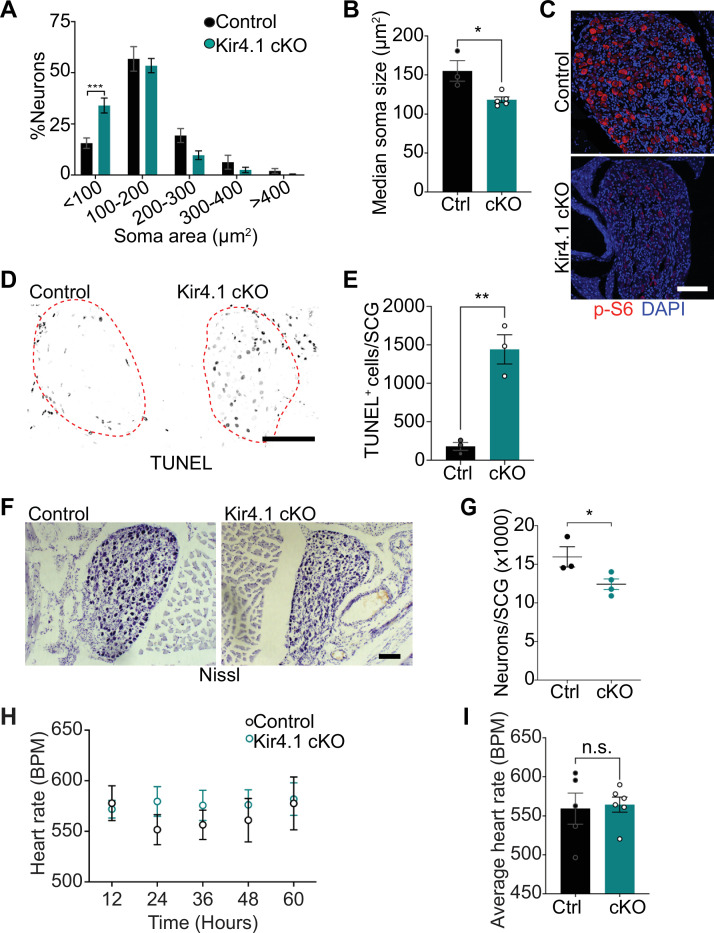
Figure 5. Defects in neuron viability in Kir4.1 cKO mice.
(A) Kir4.1 cKO sympathetic neurons have smaller soma sizes compared to control neurons. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 3 control and 5 mutant mice, ***p<0.001, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction. (B) Reduced soma size, represented as median values of soma areas (μm2) of Kir4.1 cKO sympathetic neurons compared to controls. Values are mean ± SEM from n = 3 control and 5 mutant animals, *p<0.05, t-test. (C) Decreased mTOR signaling based on p-S6 immunostaining in Kir4.1 cKO sympathetic ganglia. Scale bar: 100 μm. (D) TUNEL labeling shows increased apoptosis in Kir4.1 cKO SCG (outlined in red dashed line). Scale bar: 100 μm. (E) Quantification of apoptotic cells in control and mutant sympathetic ganglia from n = 3 mice per genotype. Data presented as mean ± SEM **p<0.01, t-test. (F, G) Decreased sympathetic neuron numbers in Kir4.1 cKO mice based on Nissl-staining and cell counts in sympathetic ganglia tissue sections. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 3 control and 4 mutant animals. *p<0.05, t-test. (H) Heart rate is unaffected by Kir4.1 deletion from satellite glia. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 5 control and 6 mutant animals, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction. (I) Average heart rate over days 4–7 post-lead implantation. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 5 control and 6 mutant animals. n.s., not significant.