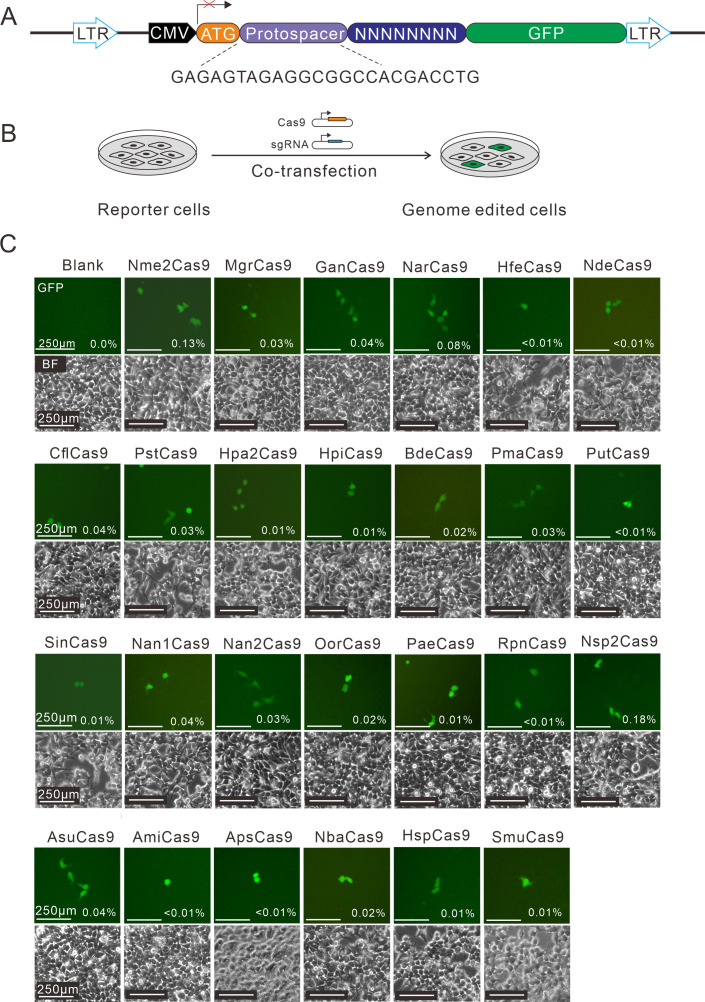
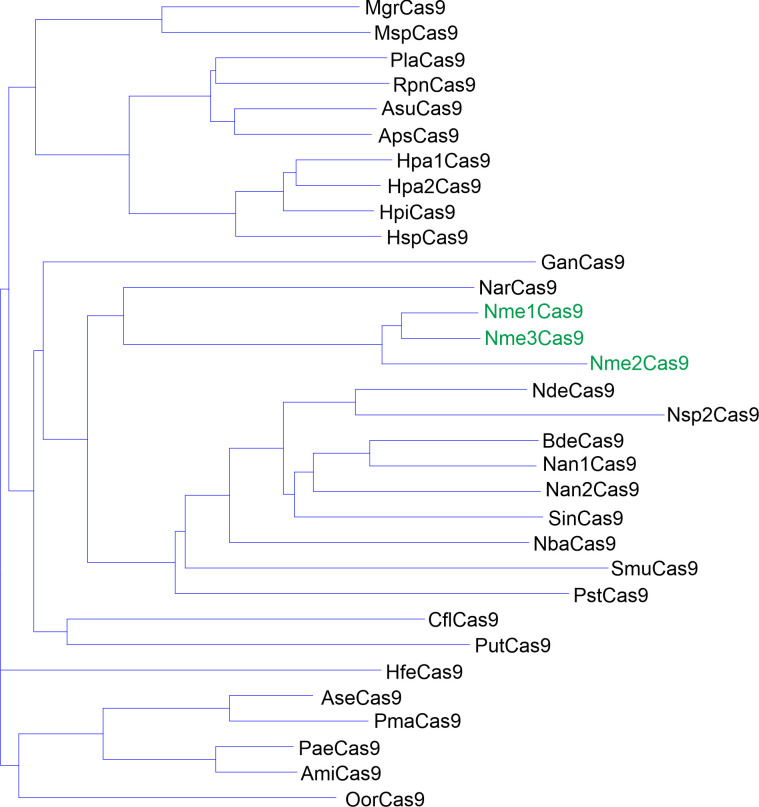
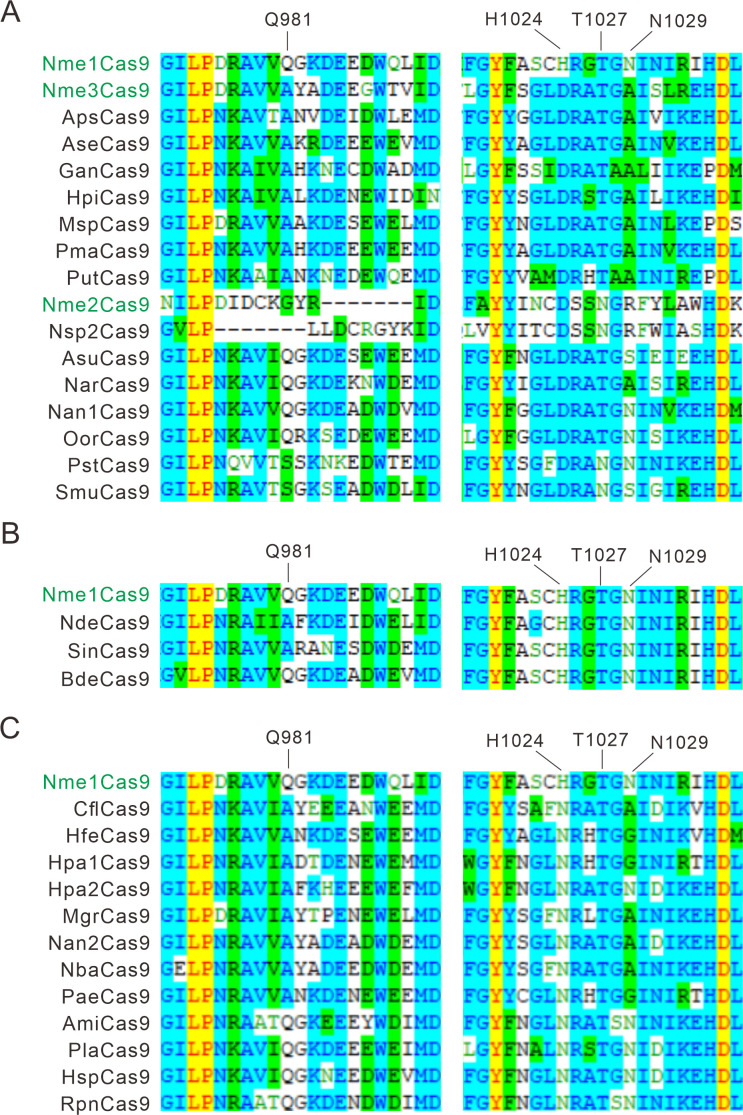
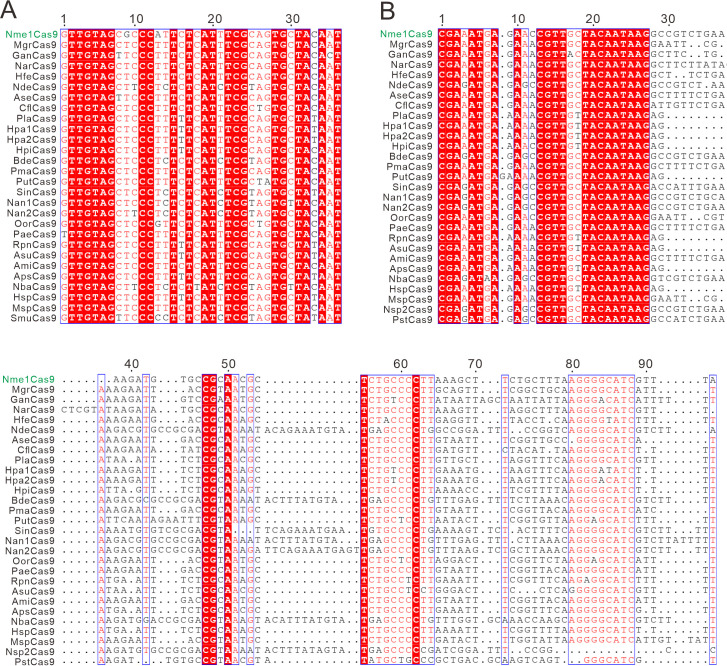
Figure 1. Screening of Nme1Cas9 orthologs activities through a GFP- activation assay.
(A) Schematic of the GFP-activation assay. A protospacer flanked by an 8 bp random sequence is inserted between the ATG start codon and GFP-coding sequence, resulting in a frameshift mutation. The library DNA is stably integrated into HEK293T cells via lentivirus infection. Genome editing can lead to in-frame mutation. The protospacer sequence is shown below. (B) The procedure of the GFP-activation assay. Cas9 and sgRNA expression plasmids were co-transfected into the reporter cells. GFP-positive cells could be observed if the protospacer is edited. (C) Twenty-five out of 29 Nme1Cas9 orthologs could induce GFP expression. The percentage of GFP-positive cells is shown. Reporter cells without Cas9 transfection are used as a negative control. Scale bar: 250 μm.