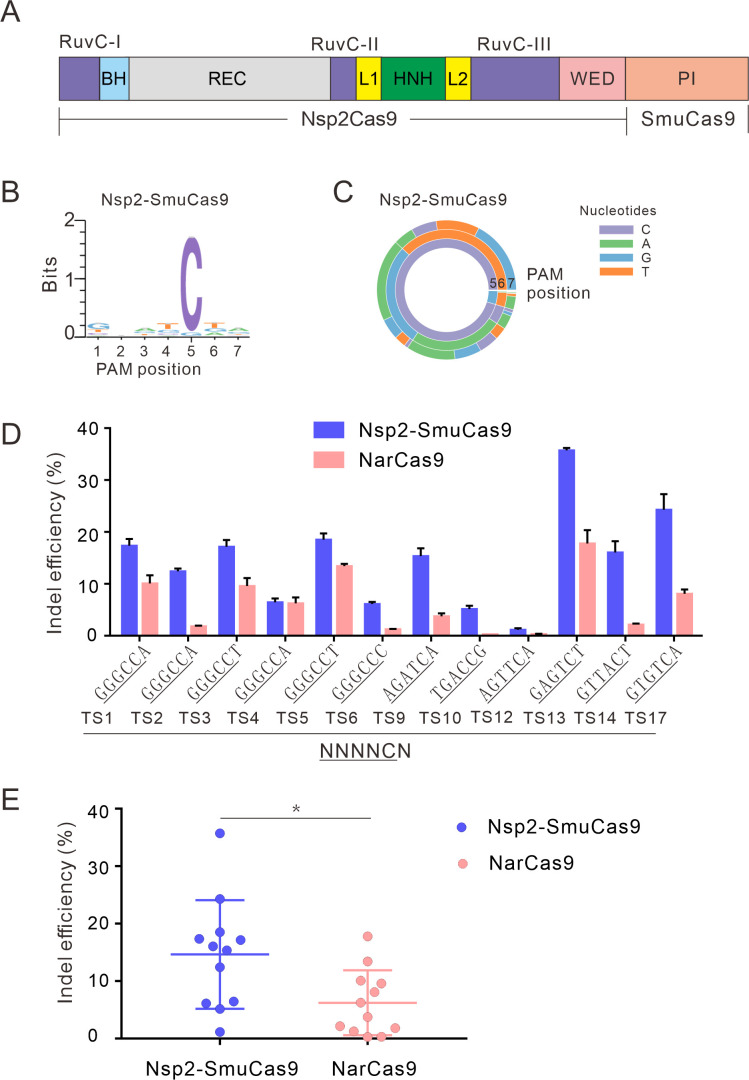
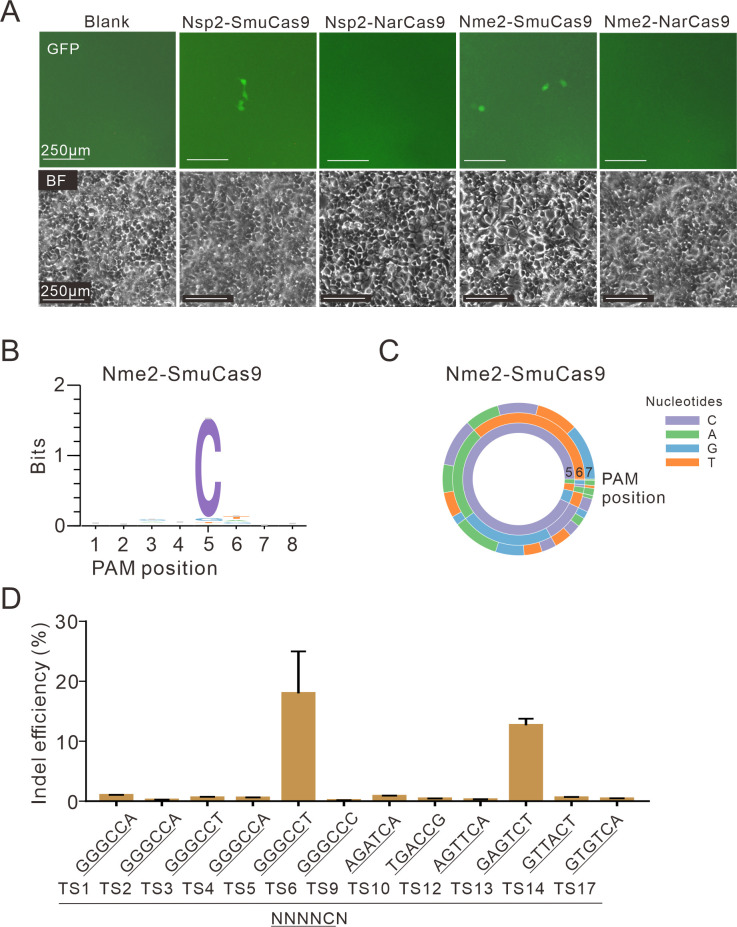
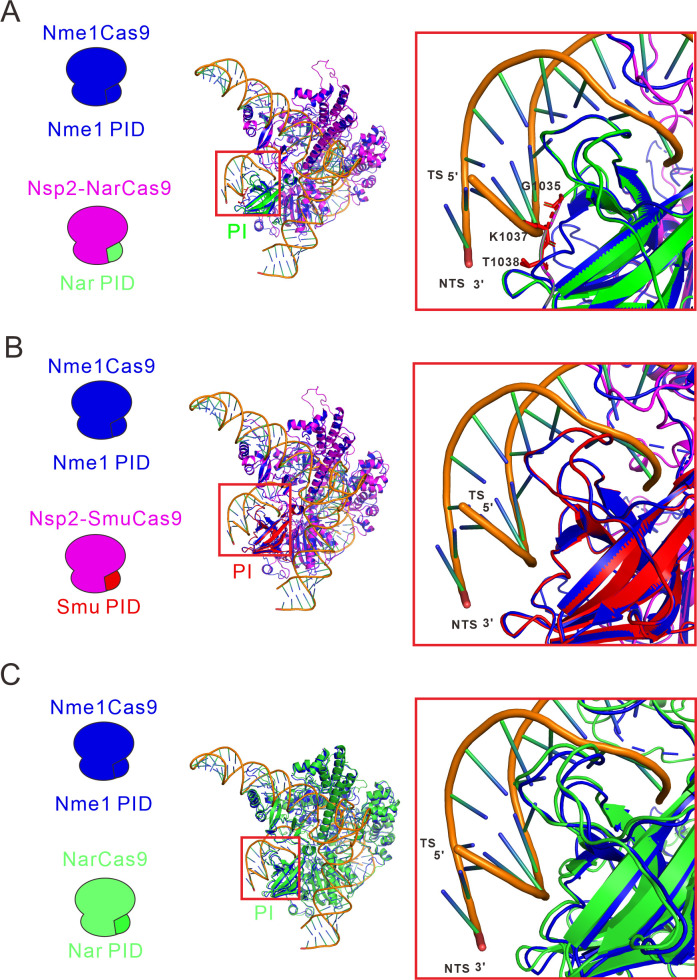
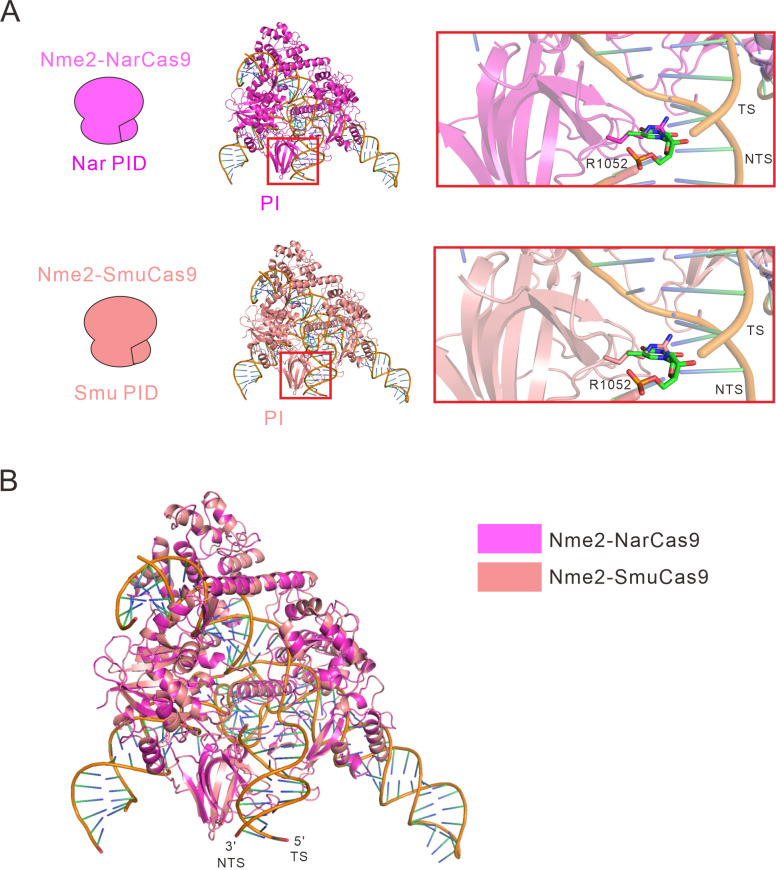
Figure 4. Characterization of Nsp2-SmuCas9 for genome editing.
(A) Schematic diagram of chimeric Cas9 nucleases based on Nsp2Cas9. PI domain of Nsp2Cas9 was replaced with the PI domain of SmuCas9. (B) Sequence logos and (C) PAM wheel diagrams indicate that Nsp2-SmuCas9 recognizes an N4C PAM. (D) Nsp2-SmuCas9 generated indels at endogenous sites with N4C PAMs in HEK293T cells. Indel efficiencies were determined by targeted deep sequencing. NarCas9 is used as a control. Data represent mean ± SD for n=3 biologically independent experiments. (E) Quantification of the indel efficiencies for Nsp2-SmuCas9 and NarCas9. Each dot represents an average efficiency for an individual locus. Data represent mean ± SD for n=3 biologically independent experiments. p values were determined using a two-sided Student’s t test. *p=0.0148 (0.01<p < 0.05).