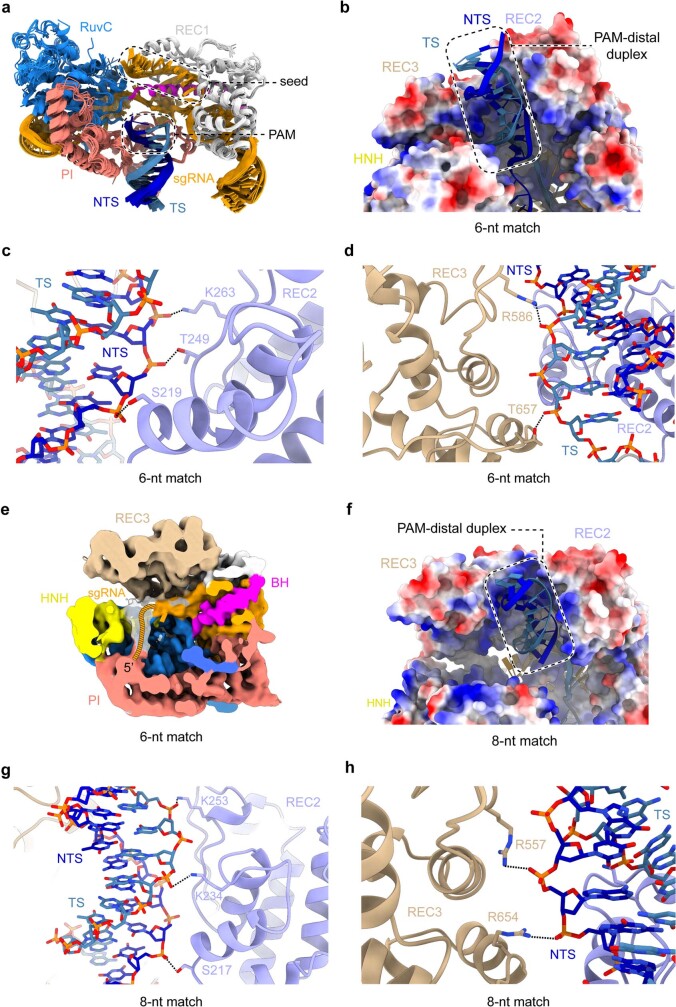
Extended Data Fig. 5. Stabilisation of the PAM-distal duplex by REC2/3 domains.
a, Structural overlays of the SpCas9 bridge helix (BH), REC1, RuvC, and PAM-interacting (PI) domains, as well as the PAM-proximal DNA duplex and the sgRNA from the partially bound complex structures determined by crystallography and cryoEM, and full R-loop complexes (PDB: 6O0X, 6O0Y, 6O0Z)28. b, Zoom-in view of the PAM-distal DNA duplex in the 6-nt match complex. The protein surface is coloured according to electrostatic surface potential, with red denoting negative and blue positive charge. c, Interactions between SpCas9 REC2 domain and the backbone of the PAM-distal NTS in the 6-nt match complex. d, Interactions between the REC3 domain and the backbone of the PAM-distal TS in the 6-nt match complex. e, Central slice through the 6-nt match complex. Cryo-EM density map is coloured according to Fig. 1a. White density indicates positioning of the 5’ sgRNA end. f, PAM-distal DNA duplex in the 8-nt match complex remains positioned in a positively charged cavity between the REC2 and REC3 domains. The protein surface is coloured according to electrostatic surface potential. g, Interactions of the REC2 domain with the PAM-distal DNA duplex in the 8-nt match complex. h, Interactions of the REC3 domain with the NTS of the PAM-distal duplex in the 8-nt match complex.