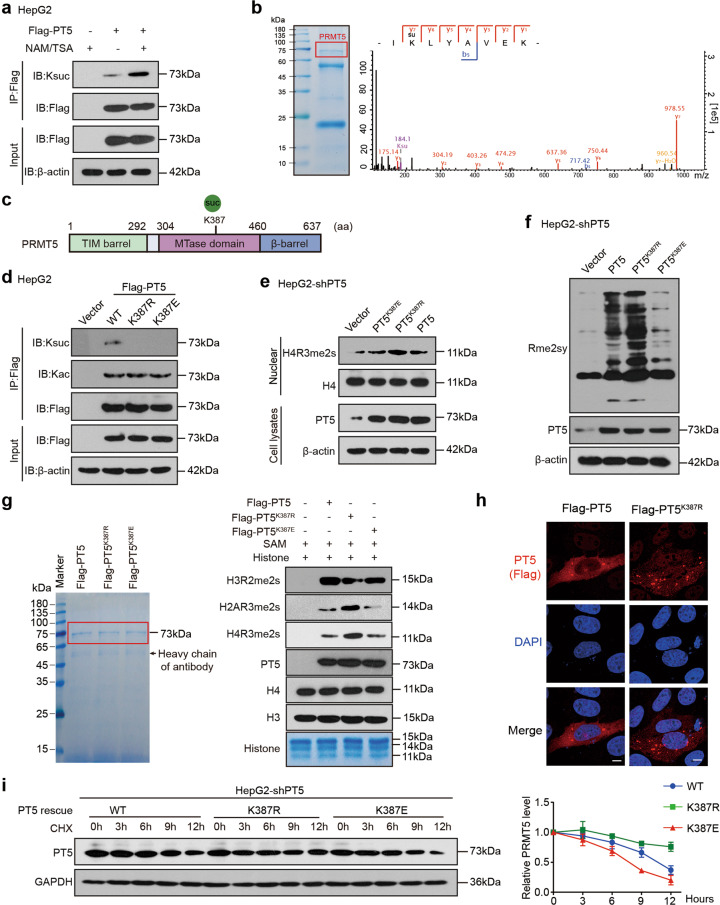
Fig. 1. Identification of succinylation of PRMT5 K387 and its role in methyltransferase activity of PRMT5.
a Succinylation levels of exogenous PRMT5 were tested by immunoprecipitation (IP) analysis in HepG2 cells treated with NAM and TSA as indicated. b Succinylation sites of PRMT5 were examined by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). PRMT5 was immunoprecipitated from HepG2 cells, and the loading proteins were stained with Coomassie blue (left panel). K represents potential succinylation sites in PRMT5 analysed by LC-MS (right panel). c A schematic model of the structure and succinylation sites of PRMT5. d The succinylation and acetylation levels of Flag-tagged PRMT5 or PRMT5 mutants were examined by IP analysis in HepG2 cells transfected with the indicated plasmids. e, f The methylation of H4R3 or global proteins was detected by Western blot analysis using H4R3me2s or Rme2sy antibodies in HepG2-shPT5 cells transfected with the indicated plasmids. g In vitro methylation assays were performed using recombinant histone proteins and purified Flag-PRMT5. Flag-tagged PRMT5 or PRMT5 mutants purified from HEK293T cells were incubated with SAM and recombinant histones. The loading of the proteins was visualised using Coomassie blue staining (left). The methylation of H4 R3, H3 R2 and H2A R3 was evaluated by Western blot analysis using H4R3me2s, H3R2me2s and H2AR3me2s antibodies (right). h The localisation of exogenous Flag-tagged PRMT5 (red) was determined by immunofluorescence staining in HepG2-shPRMT5 cells. Scale bars, 5 μm. i HepG2-shPT5 cells were transfected with WT or mutant PRMT5 plasmids, followed by treatment with cycloheximide (CHX, 100 μg/mL) for the indicated times. The levels of PRMT5 were detected by Western blot analysis (left). The quantitative analysis of PRMT5 expression is shown (right).