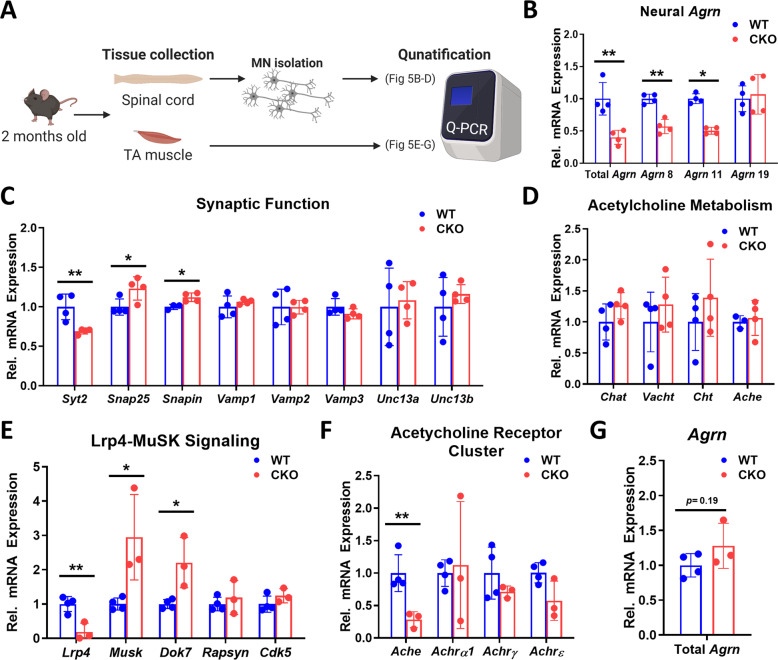
Fig. 5. Deleting Crabp1 causes deregulation in AGRIN-LRP4-MuSK signaling.
A Illustration of the experiment procedure. The spinal cord and TA muscle were collected from 2 months old mice (n = 4/group), and MNs were isolated from the spinal cord. B qPCR of total and neural Agrn expression in spinal MNs. CKO MNs express a significantly lowered level of Agrn as compared to WT MNs. C Expression of synaptic functional markers in spinal MNs. CKO MNs express a significantly lowered level of SYT2 and elevated expression of SNAP25 and SNAPIN as compared to WT. D Expression of genes for acetylcholine (ACh) metabolism in spinal MNs. E Expression of AGRIN-targeted LRP4-MuSK signaling components in TA muscle. CKO muscle expresses a significantly lowered LRP4 level, and elevated expression of MuSK and DOK7, as compared to WT. F Expression of AChE and AChRs in TA muscle. CKO muscle expresses a significantly lowered level of AChE, as compared to WT. G qPCR detect Agrn expression in WT and CKO muscle tissue. Results are presented as means ± SD, *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, compared with WT group.