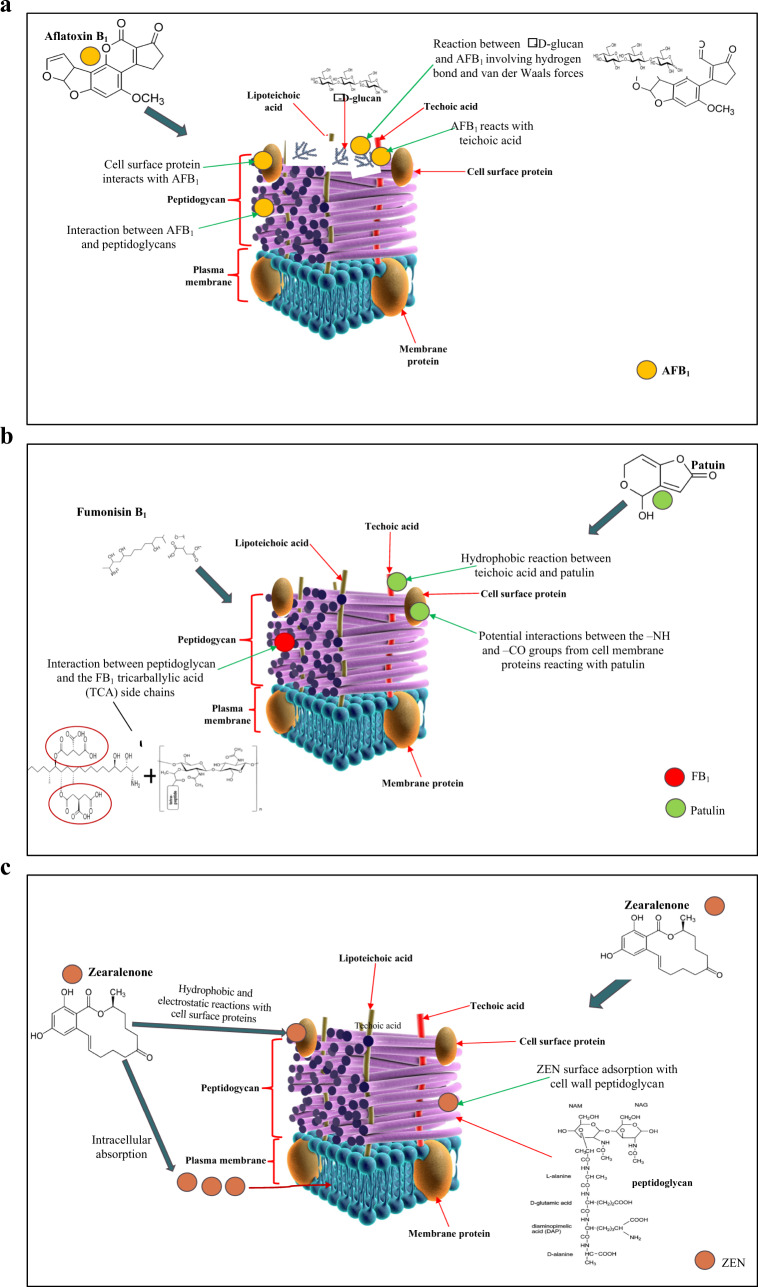
Fig. 5. Diagrams illustrating possible interactions between some selected mycotoxins and bacteria cell wall components.
a The Mechanisms of interactions between aflatoxin B1 with bacterial cell. Wall components such as peptidoglycan, cell wall teichoic acids, β-D-glucan, and cell surface proteins. Illustrations adapted from Adobe stock images, copyright Kateryna_Kon (http://stock.adobe.com/) under Standard Licensing. b The Mechanisms of interactions between fumonisin B1 and patulin with bacterial cell wall components. fumonisin B1 only reacts with cell wall peptidoglycan (interaction between tricarballyllic acid (TCA) of fumonisin B1 and peptidoglycans). The known possible mechanism for bacterial binding to patulin involves interaction with cell surface proteins (-NH or -CO groups). Illustrations adapted from Adobe stock images, copyright Kateryna_Kon (http://stock.adobe.com/) under Standard Licensing. c The Possible mechanisms of interactions between zearalenone and a LAB strain; interaction with intracellular proteins, reaction with cell wall peptidoglycans, or interaction with cell surface proteins (by hydrophobic or electrostatic reaction). Illustrations adapted from Adobe stock images, copyright Kateryna_Kon (http://stock.adobe.com/) under Standard Licensing. AFB Aflatoxin B1, ZEN Zearalenone, OTA Ochratoxin A, DON Deoxynivalenol, FB1 Fumonisin B1.